第17天-整合Redis缓存改造三级分类,并解决缓存击穿、穿透、雪崩、一致性问题
1.缓存
1.1.缓存使用
为了系统性能的提升,一般都会将部分数据放入缓存中,达到快速响应的目的。而数据库承担数据落盘工作。
哪些数据适合放入缓存?
- 即时性、数据一致性要求不高的
- 访问量大且更新频率不高的数据(读多,写少)
举例:电商类应用,商品分类,商品列表等适合缓存并加一个失效时间(根据数据更新频率来定),后台如果发布一个商品,买家需要5分钟才能看到新的商品,一般还是可以接受的。
1.2.Cache-Aside模式
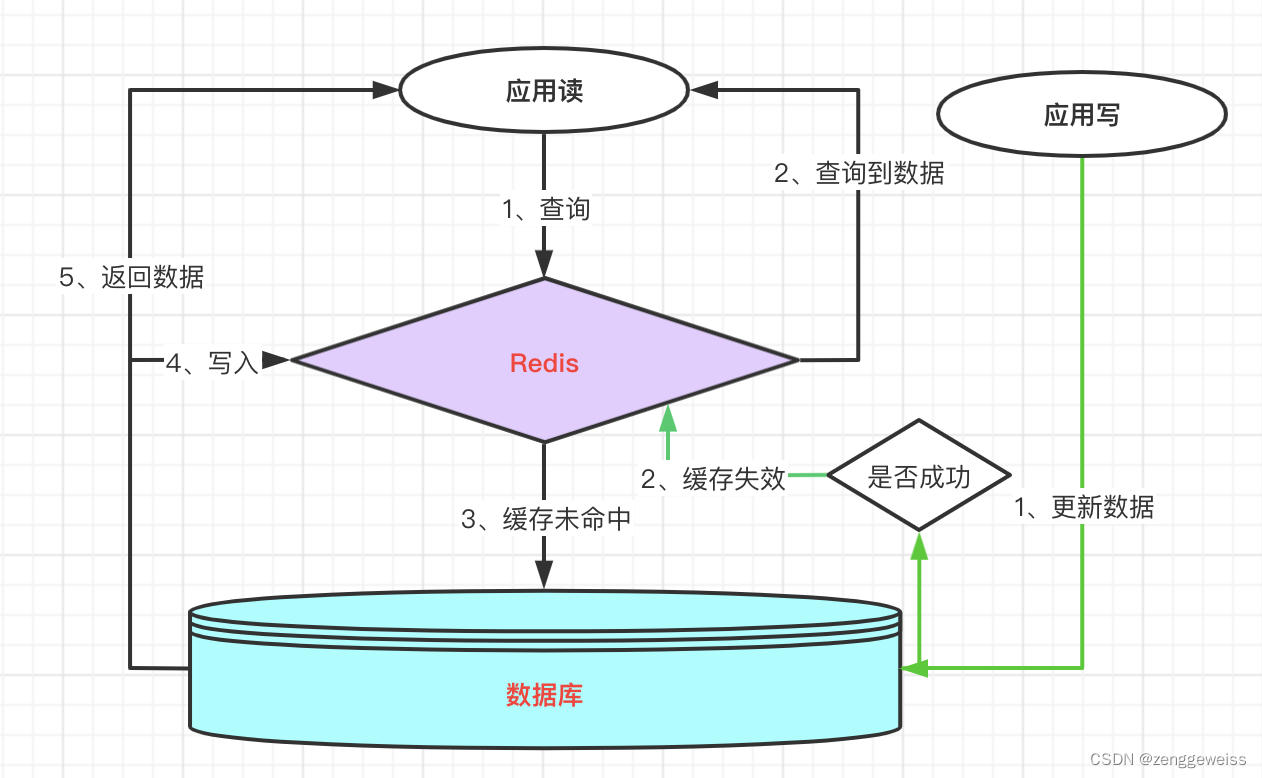
边缘缓存模式(Cache-Aside Pattern),即按需将数据从数据存储加载到缓存中。此模式最大的作用就是提高性能减少不必要的查询。
- 先从缓存查询数据
- 如果没有命中缓存则从数据存储查询
- 将数据写入缓存
业务中最常用的缓存层设计模式,基本实现逻辑和相关概念如下:
专业术语:
- 缓存命中:直接查询缓存且命中,返回数据;
- 缓存加载:查询缓存未命中,从数据库中查询数据,获取数据后并加载到缓存;
- 缓存失效:数据更新写到数据库,操作成功后,让缓存失效,查询时候再重新加载;
- 缓存穿透:查询数据库不存在的对象,也就不存在缓存层的命中;
- 缓存击穿:热点key在失效的瞬间,高并发查询这个key,击穿缓存,直接请求数据库;
- 缓存雪崩:缓存Key大批量到过期时间,导致数据库压力过大;
- 命中率:缓存设计的是否合理要看命中率,命中率高说明缓存有效抗住了大部分请求,命中率可以
- 通过Redis监控信息计算,一般来说命中率在(70-80)%都算合理。
并发问题,执行读操作未命中缓存,然后查询数据库中取数据,数据已经查询到还没放入缓存,同时一个更新写操作让缓存失效,然后读操作再把查询到数据加载缓存,导致缓存的脏数据。
在遵守缓存使用原则下出现该情况概率非常低,可以通过复杂的Paxos协议保证一致性,一般情况是不考量该场景的处理,如果缓存管理过于复杂,会和缓存层核心理念相悖。
基本描述代码
@Service
public class KeyValueServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl implements KeyValueService {@Resourceprivate RedisService redisService;@Overridepublic KeyValueEntity select(Integer id) {//查询缓存String redisKey = RedisKeyUtil.getObectKey(id) ;String value = redisService.get(redisKey) ;if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(value)){return JSON.parseObject(value, KeyValueEntity.class);}//查询库KeyValueEntity keyValueEntity = this.getById(id);if (keyValueEntity != null){//缓存写入redisService.set(redisKey, JSON.toJSONString(keyValueEntity));}//返回值return keyValueEntity ;}@Overridepublic boolean update(KeyValueEntity keyValueEntity) {//更新数据boolean updateFlag = this.updateById(keyValueEntity);//清除缓存if (updateFlag){redisService.delete(RedisKeyUtil.getObectKey(keyValueEntity.getId()));}return updateFlag ;}
}
1.3.整合Redis作为缓存
gmall-product 模块中 引入依赖
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-data-redis
配置redis
spring:redis:host: 192.168.139.10
进行压测时产生堆外内存溢出, OutOfDirectMemoryError
-
Spring Boot 2.0以后默认使用lettuce作为操作redis的客户端,它使用netty进行网络通信
-
lettuce的bug导致netty堆外内存溢出
1、netty若没有指定堆外内存,默认使用-Xmx设置的值
2、可以通过 -Dio.netty.maxDirectMemory 进行设置
解决方案
-
不能使用 -Dio.netty.maxDirectMemory 只去调大堆外内存
这样做只是延缓了出现 OutOfDirectMemoryError 的时间,系统长时间运行后,还是有可
能出现! -
升级Lettuce客户端
-
切换使用Jedis
1、从starter中排除lettuce
2、引入jedis依赖
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-data-redis io.lettuce lettuce-core redis.clients jedis Spring 支持 Redis 客户端
- Lettuce
- Jedis
RedisAutoConfiguration
@Import({ LettuceConnectionConfiguration.class,
JedisConnectionConfiguration.class })
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {}
2.三级分类数据获取优化
2.1.加入缓存
CategoryServiceImpl
@Override
public Map//优先从缓存中获取数据String catalogJson = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("catalogJson");if (StringUtils.isEmpty(catalogJson)) {//缓存中没有,则从数据库查询Map> stringListMap =JsonUtils.jsonToMapList(catalogJson, Catalog2VO.class);return stringListMap;
}
2.2.JMeter压测
-
未加索引和代码逻辑未优化
QPS:5/s -
pms_category 表给 parent_cid 字段加索引
QPS:25/s -
优化代码逻辑
QPS:395/s -
加入Redis缓存
QPS:2348/s
3.高并发下缓存失效问题
3.1.缓存穿透
key不存在
指查询一个一定不存在的数据,由于缓存没有命中,将去查询数据库,但是数据库也无此记录,我们没有将这次查询的null写入缓存,这将导致这个不存在的数据每次请求都要到存储层去查询,失去了缓存的意义
风险:利用不存在的数据进行攻击,数据库瞬时压力增大,最终导致崩溃
解决:
- null结果缓存,并加入短暂过期时间
- 布隆过滤器(Bloom Filter)
3.2.缓存雪崩
key大面积同时失效
缓存雪崩是指在我们设置缓存时,key采用了相同的过期时间,导致缓存在某一时刻同时无效,请求全部转发到DB,DB瞬时压力过重雪崩。
解决:原有的失效时间基础上增加一个随机值,比如1-5分钟随机,这样每一个缓存的过期时间的重复率就会降低,就很难引发集体失效的事件。
3.3.缓存击穿
某一个热点key失效,被高频访问
对于一些设置了过期时间的key,如果这些key可能会在某些时间点被超高并发地访问,是一种非常“热点”的数据。如果这个key在大量请求同时进来前正好失效,那么所有对这个key的数据查询都落到DB,我们称之为缓存击穿。
解决:加锁!大量并发只让一个去查,其它等待,查到以后释放锁,其它获取到锁,先查缓存,就会有数据,不用去DB。
4.分布式锁
本地锁: synchronized JUC(Lock) ,只能锁住当前进程,分布式场景下需要分布式锁。
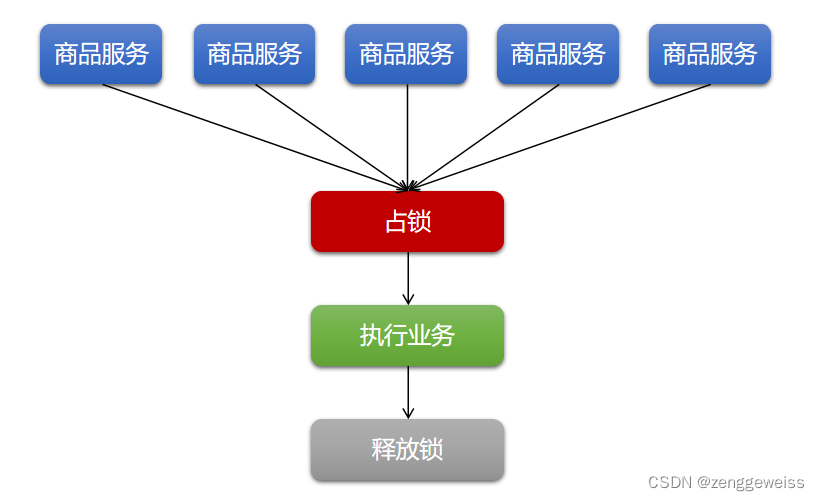
4.1.Redis分布式锁
4.1.1.实现原理
官方文档:http://www.redis.cn/commands/set.html
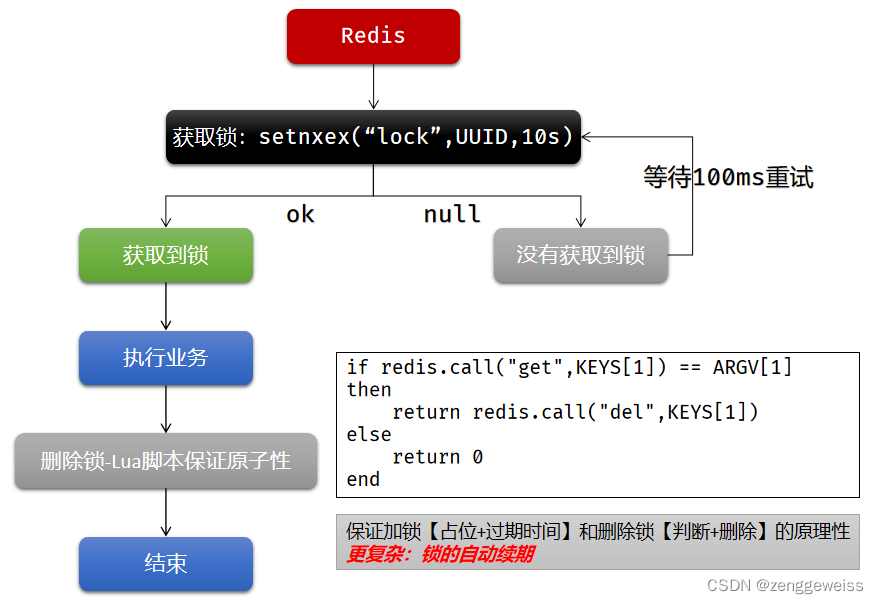
4.1.2.问题解决方案
- SET … NX 占好位,业务代码异常或者程序在页面过程中宕机,没有执行删除锁逻辑,这就造成了死锁!
解决:设置锁的自动过期时间,即使没有删除,会自动删除 - SET … NX 设置好,正要去设置过期时间,此时宕机,那就又会死锁!
解决:设置过期时间和占位必须是原子的,Redis支持使用 SET ю EX 300 NX 命令 - 删除锁直接删除?如果由于业务时间长,锁自己过期了,直接删除,有可能把别人正在持有的锁删除了。
解决:加锁的时候,值指定为UUID,每个人匹配自己的锁才能删除。 - 删锁时,如果正好判断是当前的值,正要删除锁的时候,锁已经过期,别人已经设置到新的值,那么我们删除的是别人的锁。
解决:删除锁必须保证原子性,使用Redis+Lua脚本完成
if redis.call("get",KEYS[1]) == ARGV[1]
then//删除成功返回 1return redis.call("del",KEYS[1])
else//删除失败返回 0return 0
end
String script = "if redis.call(\"get\",KEYS[1]) ڑ ARGV[1]\n" +"then\n" +" return redis.call(\"del\",KEYS[1])\n" +"else\n" +" return 0\n" +"end";
redisTemplate.execute(new DefaultRedisScript(script, Integer.class),Arrays.asList("lock"),uuid);
总结:
-
加锁保证原子性
SET key value NX EX max-lock-time -
删除保证原子性
使用Lua脚本,而不是使用DEL命令 -
自动续期
没有提供
4.2.Redisson
4.2.1.介绍
https://github.com/redisson/redisson
Redisson底层的所有锁都保证了原子性,使用了Lua脚本来执行,还使用了看门狗机制进行自动续期
4.2.2.引入依赖
org.redisson redisson 3.14.1
https://github.com/redisson/redisson/tree/master/redisson-spring-boot-starter
org.redisson redisson-spring-boot-starter 3.14.0
4.2.3.可重入锁(Reentrant Lock)
@GetMapping("/testLock")
public String testLock(){RLock rLock = redisson.getLock("anyLock");//加锁,阻塞式等待,默认加锁都是30s时间//1. 看门狗机制:锁的自动续期,如果业务超长,运行期间自动给锁续上新的30s,不用担心业务时间长,锁自动过期被删掉//2. 加锁的业务只要运行完成,就不会给当前锁续期,即使不手动解锁,锁默认在30s以后自动删除rLock.lock();//10s自动解锁,自动解锁时间一定要大于业务的执行时间,没有看门狗机制rLock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//问题:rLock.lock(10, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 在锁时间到期以后,不会自动续期//1. 如果我们传递了锁的过期时间,就发送给redis执行脚本,进行占锁,默认时间就是我们指定的时间//2. 如果我们未指定锁的超时时间,就使用30 * 1000(LockWatchdogTimeout 看门狗的默认时间)//- 只要占锁成功,就会启动一个定时任务(重新给锁设置过期时间,新的过期时间就是看门狗的默认时间)//- 定时任务调度间隔,internalLockLeaseTime(看门狗时间) / 3,每隔10s都会自动再次续期为30s//最佳实战//1. rLock.lock(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS); 省掉了整个续期操作,手动解锁try{System.out.println("加锁成功,执行业务 ..."+Thread.currentThread().getId());Thread.sleep(30000);}catch(Exception e){}finally{System.out.println("释放锁 ..."+Thread.currentThread().getId());//解锁rLock.unlock();}
}
4.2.4.读写锁(Read Write Lock)
保证一定能读到最新数据
- 写锁是一个排他锁(互斥锁、独享锁)
- 读锁是一个共享锁
- 写锁没释放,读就必须等待
- Read + Read:相当于无锁,并发读只会在redis中记录好所有当前的读锁,他们都会同时加锁成功
- Write + Read:等待写锁释放
- Write + Write:阻塞方式
- Read + Write:有读锁,写也需要等待
@GetMapping("/testWrite")
public String testWrite(){RReadWriteLock lock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("rw-lock");//修改数据加写锁RLock rLock = lock.writeLock();rLock.lock();String s = "";try {System.out.println("写锁加锁成功 ... "+Thread.currentThread().getId());s = UUID.randomUUID().toString();Thread.sleep(30000);redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("orderId", s)} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {rLock.unlock();System.out.println("写锁释放成功 ... "+Thread.currentThread().getId());}return s;
}@GetMapping("/testRead")
public String testRead(){RReadWriteLock lock = redisson.getReadWriteLock("rw-lock");//读数据加读锁RLock rLock = lock.readLock();rLock.lock();String s = "";try {System.out.println("读锁加锁成功 ..."+Thread.currentThread().getId());s = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("orderId");} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {rLock.unlock();System.out.println("读锁释放成功 ... "+Thread.currentThread().getId());}return s;
}
4.2.5.闭锁(CountDownLatch)
场景:学校放假,锁大门。必须要等到学校所有班级都走完了,才可以锁大门!
@GetMapping("/lockDoor")
public String lockDoor(){RCountDownLatch countDownLatch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("door");//设置学校有5个班级countDownLatch.trySetCount(5);//等待闭锁都完成countDownLatch.await();return "放假了 ... ";
}@GetMapping("/go/{id}")
public String go(@PathVariable("id") Long id){RCountDownLatch countDownLatch = redisson.getCountDownLatch("door");//计数-1countDownLatch.countDown();return id + "班的人都走了 ... "
}
4.2.6.信号量(Semaphore)
场景:车库停车,占用车位和释放车位
@GetMapping("/park")
public String park(){RSemaphore semaphore = redisson.getSemaphore("park");//获取一个信号(占一个车位),阻塞式等待semaphore.acquire();return "ok";
}@GetMapping("/go")
public String go(){RSemaphore semaphore = redisson.getSemaphore("park");//释放一个信号(释放一个车位)semaphore.release();return "ok";
}
分布式限流场景
//若获取不到信号量,则立即返回false,不阻塞等待
boolean b = semaphore.tryAcquire();
if(b) {//执行业务
} else {return "error ... ";
}
4.3.三级分类数据加锁解决缓存击穿
public Map> getCatalogJsonFromDbWithLock() {RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock("catalogJsonLock");lock.lock();MapcatalogJsonFromDb = getCatalogJsonFromDb();} finally {lock.unlock();}return catalogJsonFromDb;
}
5.缓存数据一致性
5.1.双写模式
- 写数据库
- 更新缓存
5.2.失效模式(推荐)
- 写数据库
- 删除缓存
在高并发情况下就会有可能出现数据一致性问题!
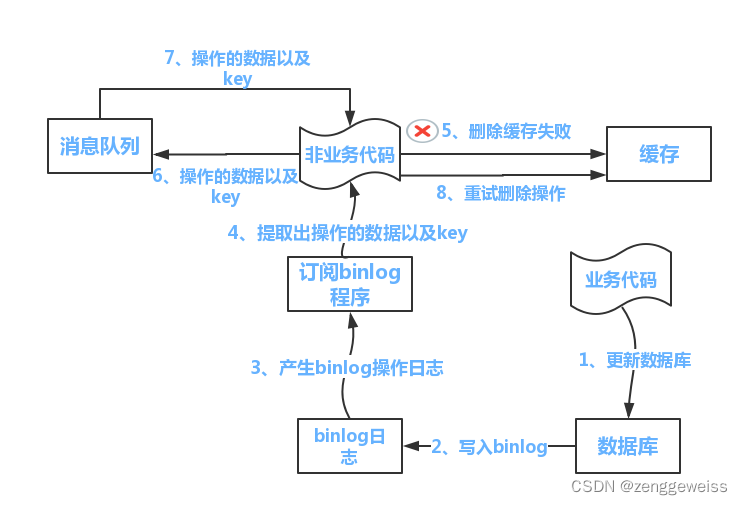
解决方案:
- 如果是用户纬度数据(订单数据、用户数据),这种并发几率非常小,不用考虑这个问题,缓存数据加上过期时间,每隔一段时间触发读的主动更新即可。
- 如果是菜单,商品介绍等基础数据,可以不用太考虑数据实时性问题,(若真要考虑实时性,可以去使用canal订阅binlog的方式)。
- 缓存数据+过期时间也足够解决大部分业务对于缓存的要求。
- 通过加锁保证并发读写,写写的时候按顺序排好队,读读无所谓,所以适合使用读写锁。(业务不关心脏数据,允许临时脏数据可忽略)。
总结:
- 我们能放入缓存的数据本就不应该是实时性、一致性要求超高的。所以缓存数据的时候加上过期时间,保证每天拿到当前最新数据即可。
- 我们不应该过度设计,增加系统的复杂性。
- 遇到实时性、一致性要求高的数据,就应该查数据库,即使慢点。
6.简化缓存开发
6.1.Spring Cache简介
文档:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/reference/html/integration.html#cache
Spring从3.1开始定义了 org.springframework.cache.Cache 和
org.springframework.cache.CacheManager 接口来统一不同的缓存技术,并支持使用
JCache(JSR-107)注解简化开发;
Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义。包含缓存的各种操作集合。Cache接口下 Spring 提供了各种xxxCache 的实现,如 RedisCache , EhCacheCache , ConcurrentMapCache 等;
每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查指定参数的目标方法是否已经被调用过,如果有就直接从缓存中获取方法调用后的结果,如果没有就调用方法并缓存结果后返回给用户,下次调用直接从缓存中获取。
使用Spring缓存抽象时我们需要关注以下两点:
- 确定方法需要被缓存以及他们的缓存策略
- 从缓存中读取之前缓存存储的数据
6.2.整合SpringCache简化缓存开发
6.2.1.引入依赖
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-cache
org.springframework.boot spring-boot-starter-data-redis
6.2.2.配置
自动配置了哪些?
- CacheAutoConfiguration 会导入 RedisCacheConfiguration
- 自动配置好缓存管理器 RedisCacheManager
配置使用redis作为缓存
spring:cache:type: redis
6.2.3.开启缓存功能
@EnableCaching
@EnableCaching
@SpringBootApplication
public class GmallProductApplication {}
6.2.4.Spring Cache 注解
- @Cacheable : Triggers cache population. 触发将数据保存到缓存的操作
- @CacheEvict : Triggers cache eviction. 触发将数据从缓存删除的操作(失效模式)
- @CachePut : Updates the cache without interfering with the method execution. 不影响方法执行更新缓存 (双写模式)
- @Caching : Regroups multiple cache operations to be applied on a
method. 组合以上多个操作 - @CacheConfig : Shares some common cache-related settings at
class-level. 在类级别共享缓存的相同配置
6.2.5.最佳实践
每一个需要缓存的数据都指定缓存名字(缓存的分区,按照业务类型分)
@Cacheable({“category”}) 表示当前方法的结果需要缓存,如果缓存中有,方法不会调用。如果缓存中没有,会调用方法,最后将方法的结果放入缓存。
@Cacheable({"category"})
@Override
public List getLevel1Categories() {List entities = list(new QueryWrapper().eq("parent_cid", 0));return entities;
}
默认行为:
- 如果缓存中有数据,方法不会调用
- key默认自动生成,值为 simpleKey
- 缓存的value的值,默认使用jdk序列化机制,将序列化后的数据存到redis(不是json)
- 默认TTL时间 -1
自定义:
- 指定生成的缓存使用的key,key属性指定,接受一个SpEL,参考:https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/integration.html#cache-spel-context
@Cacheable(value = {"category"}, key = "#root.methodName")
@Cacheable(value = {"category"}, key = "#root.method.name")
- 指定缓存数据的TTL,在配置文件中定义 spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=3600000 (单位毫秒)
- 将数据保存为json格式,为Spring容器中放入 RedisCacheConfiguration 实例
package com.atguigu.gmall.product.config;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.cache.CacheProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;/*** 缓存配置 {@link CacheConfig}* @author zhangwen* @email: 1466787185@qq.com*/
@EnableConfigurationProperties(CacheProperties.class)
@EnableCaching
@Configuration
public class CacheConfig {/*** Redis 缓存配置* @param cacheProperties* @return*/
@Bean
public RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration(CacheProperties cacheProperties) {RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();//设置keyconfig = config.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()));//设置value值返回jsonconfig = config.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));//将配置文件中的所有配置生效CacheProperties.Redis redisProperties = cacheProperties.getRedis();if (redisProperties.getTimeToLive() != null) {config = config.entryTtl(redisProperties.getTimeToLive());}if (redisProperties.getKeyPrefix() != null) {config = config.prefixCacheNameWith(redisProperties.getKeyPrefix());}if (!redisProperties.isCacheNullValues()) {config = config.disableCachingNullValues();}if (!redisProperties.isUseKeyPrefix()) {config = config.disableKeyPrefix();}return config;}
}
6.2.6.删除缓存
@CacheEvict
@CacheEvict(value = {"category"}, key = "'getLevel1Categories'")
public void updateCascade(CategoryEntity category) {}
6.2.7.批量删除缓存
同时进行多个缓存数据 @Caching
@Caching(evict = {@CacheEvict(value = {"category"}, key = "'getLevel1Categories'"),@CacheEvict(value = {"category"}, key = "'getCatalogJson'")
})
public void updateCascade(CategoryEntity category) {}
指定删除某个分区下的所有缓存数据 @CacheEvict
@CacheEvict(value = "category", allEntries = true)
public void updateCascade(CategoryEntity category) {}
6.2.8.Spring Cache不足
读模式:
-
缓存穿透:查询一个null数据
解决:缓存空数据, spring.cache.redis.cache-null-values=true
-
缓存击穿:大量并发进来同时查询一个正好过期的数据
解决:加锁,默认是没有加锁的, sync = true 加锁解决缓存击穿
@Cacheable(value = {"category"}, key = "#root.method.name", sync = true)
-
缓存雪崩:大量的key同时过期
解决:加过期时间, spring.cache.redis.time-to-live=3600000
写模式:(缓存与数据库一致性)
- 读写加锁(读多写少场景)
- 引入Canal,感知到MySQL的更新,再将更新数据刷入缓存
- 读多写多,直接去数据库查询就行
总结:
- 常规数据(读多写少,即时性,一致性要求不高的数据),完全可以使用Spring Cache,写模式只要缓存的数据有过期时间就可以了
- 特殊数据:特殊设计(分布式锁、Canal等)