算法练习-链表(二)
算法练习-链表(二)
文章目录
- 算法练习-链表(二)
- 1. 奇偶链表
- 1.1 题目
- 1.2 题解
- 2. K 个一组翻转链表
- 2.1 题目
- 2.2 题解
- 3. 剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
- 3.1 题目
- 3.2 题解
- 3.2.1 解法1
- 3.2.2 解法2
- 4. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
- 4.1 题目
- 4.2 题解
- 4.2.1 解法1
- 4.2.2 解法2
- 5. 相交链表
- 5.1 题目
- 5.2 题解
- 6. 环形链表
- 6.1 题目
- 6.2 题解
1. 奇偶链表
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/odd-even-linked-list
1.1 题目
给定单链表的头节点 head ,将所有索引为奇数的节点和索引为偶数的节点分别组合在一起,然后返回重新排序的列表。
第一个节点的索引被认为是 奇数 , 第二个节点的索引为 偶数 ,以此类推。
请注意,偶数组和奇数组内部的相对顺序应该与输入时保持一致。
你必须在 O(1) 的额外空间复杂度和 O(n) 的时间复杂度下解决这个问题。
示例 1:
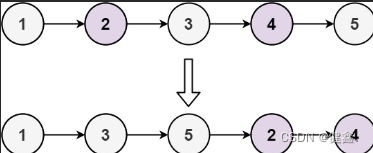
输入: head = [1,2,3,4,5]
输出: [1,3,5,2,4]
示例 2:
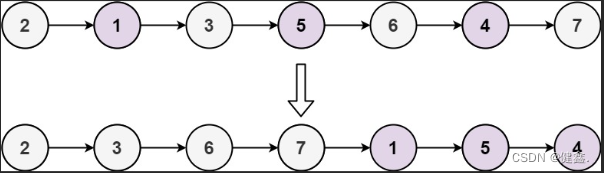
输入: head = [2,1,3,5,6,4,7]
输出: [2,3,6,7,1,5,4]
1.2 题解
创建两个链表,分别存储奇链表和偶链表,最后进行连接
由于没有新创建节点进行插入,所以满足题目空间复杂度O(1)的要求
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode oddEvenList(ListNode head) {ListNode newHead1 = new ListNode();ListNode newHead2 = new ListNode();ListNode tail1 = newHead1;ListNode tail2 = newHead2;if (head == null) {return null;}int count = 1;ListNode p = head;while (p != null) {ListNode tmp = p.next;if (count % 2 == 1) {p.next = null;tail1.next = p;tail1 = tail1.next;} else {p.next = null;tail2.next = p;tail2 = tail2.next;}count++;p = tmp;}tail1.next = newHead2.next;return newHead1.next;}
}
2. K 个一组翻转链表
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group
2.1 题目
给你链表的头节点 head ,每 k 个节点一组进行翻转,请你返回修改后的链表。
k 是一个正整数,它的值小于或等于链表的长度。如果节点总数不是 k 的整数倍,那么请将最后剩余的节点保持原有顺序。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际进行节点交换。
示例 1:
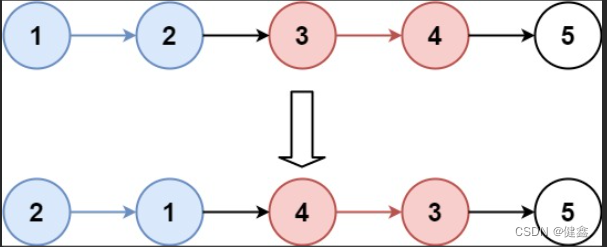
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 2
输出:[2,1,4,3,5]
示例 2:
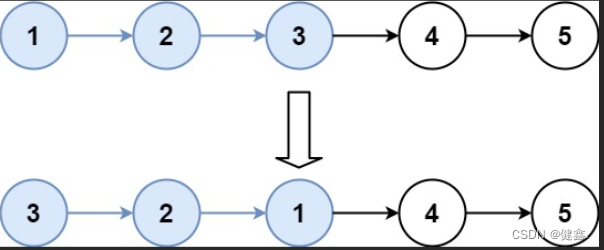
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], k = 3
输出:[3,2,1,4,5]
2.2 题解
创建一个新的头节点,将反转后的链表接入头节点,只需考虑细节方面的问题
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) {ListNode newHead = new ListNode();ListNode tail = newHead;ListNode p = head;while (p != null) {int count = 0;ListNode q = p;while (q != null) {count++;if (count == k) {break;}q = q.next;}if (q == null) {tail.next = p;return newHead.next;} else {ListNode tmp = q.next;ListNode[] nodes = reverse(p, q);tail.next = nodes[0];tail = nodes[1];p = tmp;}}return newHead.next;}public ListNode[] reverse(ListNode head, ListNode tail) {ListNode pre = null;ListNode cur = head;while (cur != tail) {ListNode tmp = cur.next;cur.next = pre;pre = cur;cur = tmp;}tail.next = pre;return new ListNode[]{tail, head};}
}
3. 剑指 Offer 22. 链表中倒数第k个节点
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/lian-biao-zhong-dao-shu-di-kge-jie-dian-lcof
3.1 题目
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。
例如,一个链表有 6 个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是 1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的倒数第 3 个节点是值为 4 的节点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 k = 2.
返回链表 4->5.
3.2 题解
3.2.1 解法1
先遍历链表,找出链表长度n,然后找正数第 n - k + 1 个节点
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {ListNode newHead = new ListNode();newHead.next = head;ListNode p = newHead;int num = 0;while (p.next != null) {p = p.next;num++;}int n = num - k ;while(n != 0) {head = head.next;n--;}return head;}
}
3.2.2 解法2
先让快指针走到第k的位置,然后快慢指针一起移动
当快指针走到头,慢指针所在的位置为倒数第k个节点
class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;int count = 0;while (fast != null) {count++;if (count == n) {break;}fast = fast.next;}if (fast == null) {return null;}fast = fast.next;while (fast.next != null) {slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;}return slow;}
}
4. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/remove-nth-node-from-end-of-list
4.1 题目
给你一个链表,删除链表的倒数第 n 个结点,并且返回链表的头结点。
示例 1:
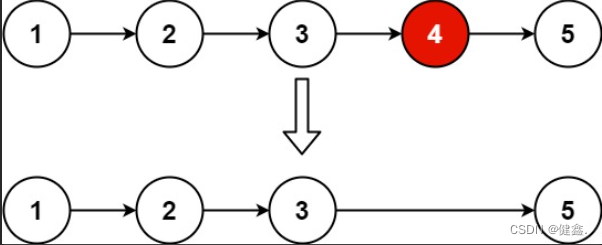
输入:head = [1,2,3,4,5], n = 2
输出:[1,2,3,5]
示例 2:
输入:head = [1], n = 1
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:head = [1,2], n = 1
输出:[1]
4.2 题解
所有方法同3,只是增加了删除操作
4.2.1 解法1
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode newHead = new ListNode();newHead.next = head;ListNode p = newHead;int m = 0;while (p.next != null) {p = p.next;m++;}p = newHead;int num = m - n;while (num != 0) {p = p.next;num--;}p.next = p.next.next;return newHead.next;}
}
4.2.2 解法2
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode() {}* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }* }*/
class Solution {public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {ListNode fast = head;ListNode slow = head;int count = 0;while (fast != null) {count++;if (count == n) {break;}fast = fast.next;}if (fast == null) {return head;}ListNode pre = null;while (fast.next != null) {pre = slow;slow = slow.next;fast = fast.next;}if (pre == null) {head = head.next;} else {pre.next = slow.next;}return head;}
}
5. 相交链表
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/intersection-of-two-linked-lists
5.1 题目
给你两个单链表的头节点 headA 和 headB ,请你找出并返回两个单链表相交的起始节点。如果两个链表不存在相交节点,返回 null 。
图示两个链表在节点 c1 开始相交:
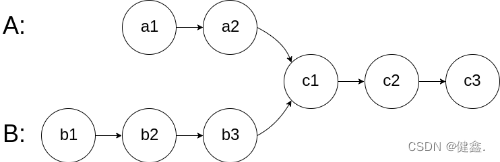
题目数据 保证 整个链式结构中不存在环。
注意,函数返回结果后,链表必须 保持其原始结构 。
自定义评测:
评测系统 的输入如下(你设计的程序 不适用 此输入):
intersectVal - 相交的起始节点的值。如果不存在相交节点,这一值为 0
listA - 第一个链表
listB - 第二个链表
skipA - 在 listA 中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
skipB - 在 listB 中(从头节点开始)跳到交叉节点的节点数
评测系统将根据这些输入创建链式数据结构,并将两个头节点 headA 和 headB 传递给你的程序。如果程序能够正确返回相交节点,那么你的解决方案将被 视作正确答案 。
示例 1:
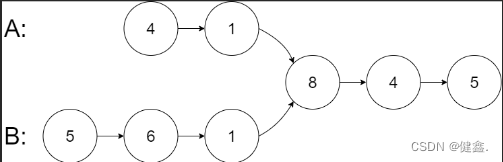
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,6,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3
输出:Intersected at ‘8’
解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,6,1,8,4,5]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
— 请注意相交节点的值不为 1,因为在链表 A 和链表 B 之中值为 1 的节点 (A 中第二个节点和 B 中第三个节点) 是不同的节点。换句话说,它们在内存中指向两个不同的位置,而链表 A 和链表 B 中值为 8 的节点 (A 中第三个节点,B 中第四个节点) 在内存中指向相同的位置。
示例 2:
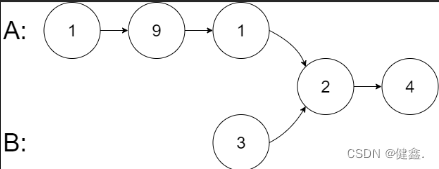
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [1,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1
输出:Intersected at ‘2’
解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。
从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [1,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。
在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
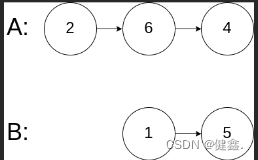
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2
输出:null
解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。
由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。
这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null 。
5.2 题解
两指针分别从两个链表头遍历,到达链表结尾之后,转移到另一个链表的表头
如果两个指针相遇,则两链表相交
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* public class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {ListNode newHeadA = new ListNode();ListNode newHeadB = new ListNode();newHeadA.next = headA;newHeadB.next = headB;ListNode p = newHeadA;ListNode q = newHeadB;int a = 0;int b = 0;while (p.next != q.next && a != 2 && b != 2) {if (p.next == null) {p = newHeadB;a++;} else {p = p.next;}if (q.next == null) {q = newHeadA;b++; } else {q = q.next;}}if (a == 2 || b == 2) {return null;}return p.next;}
}
6. 环形链表
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/linked-list-cycle
6.1 题目
给你一个链表的头节点 head ,判断链表中是否有环。
如果链表中有某个节点,可以通过连续跟踪 next 指针再次到达,则链表中存在环。 为了表示给定链表中的环,评测系统内部使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。注意:pos 不作为参数进行传递 。仅仅是为了标识链表的实际情况。
如果链表中存在环 ,则返回 true 。 否则,返回 false 。
示例 1:
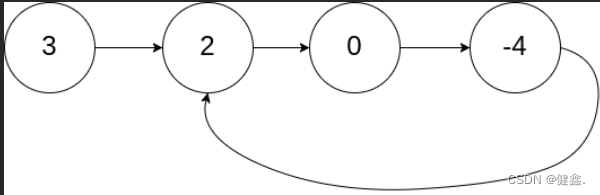
输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第二个节点。
示例 2:
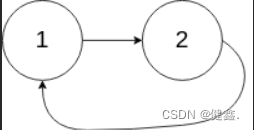
输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0
输出:true
解释:链表中有一个环,其尾部连接到第一个节点。
示例 3:

输入:head = [1], pos = -1
输出:false
解释:链表中没有环。
6.2 题解
快慢指针,如果两指针可以相遇,则该链表尾环形链表
/*** Definition for singly-linked list.* class ListNode {* int val;* ListNode next;* ListNode(int x) {* val = x;* next = null;* }* }*/
public class Solution {public boolean hasCycle(ListNode head) {ListNode newHead = new ListNode();newHead.next = head;ListNode low = newHead;ListNode fast = newHead;while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {low = low.next;fast = fast.next.next; if (fast == low) {return true;}}return false;}
}
下一篇:基于Redis实现的分布式锁