C++回顾(十一)—— 动态类型识别和抽象类
创始人
2024-05-30 06:26:19
0次
11.1 动态类识别
11.1.1 自定义类型
-
C++中的多态根据实际的对象类型调用对应的函数
(1)可以在基类中定义虚函数返回具体的类型信息
(2)所有的派生类都必须实现类型相关的虚函数
(3)每个类中的类型虚函数都需要不同的实现

-
使用虚函数进行动态类型识别的缺陷
(1)必须从基类开始提供类型虚函数
(2)所有派生类都必须重写类型虚函数
(3)每个派生类的ID必须唯一
示例代码:
#include using namespace std;class Parent
{
private:int a;
public:enum {ID = 0};virtual int getID(){return ID; }
};class Child : public Parent
{
public:enum {ID = 1};int array[102400];virtual int getID(){return ID;}};void f(Parent *p)
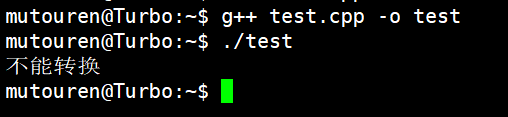
{//Child *c = (Child *)p; //派生类指针指向基类对象 //如果指针指向派生类对象,可以转换,指向基类对象,不能转换if (p->getID() == Child::ID) //如果成立,说明指向派生类对象{Child *c = (Child *)p;c->array[102400 - 1] = 100;}else{cout << "不能转换" << endl;}
}int main()
{//Parent *p = new Child;Parent *p = new Parent;f(p);return 0;
}
运行结果:
11.1.2 dynamic_cast
-
新的关键字 dynamic_cast
(1)dynamic_cast是C++中的新型关键字
(2)dynamic_cast用于基类和派生类之间的转换
(3)dynamic_cast要求使用的目标类型是多态的
即要求所在类族至少有一个虚函数
用于指针转换时,转换失败返回空指针
用于引用转换时,转换失败将引发bad_cast异常 -
dynamic_cast的优势
(1)不用显示的声明和定义虚函数
(2)不用为类族中的每个类分配类型ID -
dynamic_cast的缺陷
只能用于有虚函数的类族

示例代码:
#include using namespace std;class Parent
{
private:int a;
public:virtual void show(){}
};class Child : public Parent
{
public:int array[102400];void show(){}
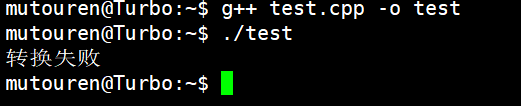
};void f(Parent *p)
{Child *c = dynamic_cast(p); //如果p指向的是基类对象,则转换失败,转换失败返回NULLif (NULL == c){cout << "转换失败" << endl;}else{cout << "转换成功" << endl;c->array[102400 - 1] = 100;}
}int main()
{//Parent *p = new Child;Parent *p = new Parent;f(p);return 0;
}
运行结果:
11.1.3 typeid
- C++提供了typeid关键字用于动态获取类型信息
(1)typeid关键字返回对应参数的类型信息
(2)typeid关键字返回一个type_info类对象,当typeid参数为NULL时,抛出bad_typeid异常
(3)type_info类的使用需要包含typeinfo头文件 - typeid的使用
示例代码:
#include
#include using namespace std;class Parent
{
private:int a;
public:virtual void show(){}
};class Child : public Parent
{
public:int array[102400];
public:void show(){}
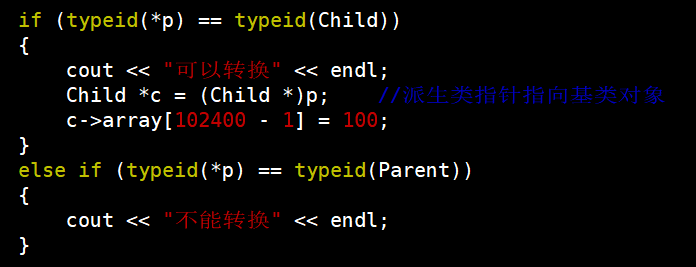
};void f(Parent *p)
{if (typeid(*p) == typeid(Child)){cout << "可以转换" << endl;Child *c = (Child *)p; //派生类指针指向基类对象c->array[102400 - 1] = 100;}else if (typeid(*p) == typeid(Parent)){cout << "不能转换" << endl;}
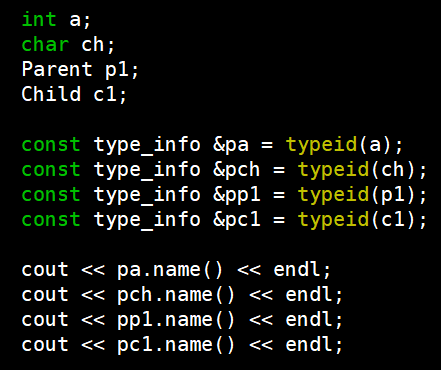
}int main()
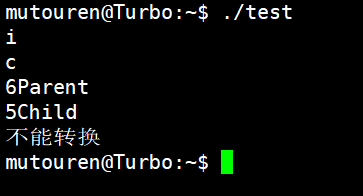
{int a;char ch;Parent p1;Child c1;const type_info &pa = typeid(a); const type_info &pch = typeid(ch); const type_info &pp1 = typeid(p1); const type_info &pc1 = typeid(c1); cout << pa.name() << endl;cout << pch.name() << endl;cout << pp1.name() << endl;cout << pc1.name() << endl;//if (pa.name() == i) // 不同编译器可以不一样(不能这么写)Parent *p = new Parent;//Parent *p = new Child;f(p);return 0;
}
运行结果:
11.2 纯虚函数和抽象类
11.2.1 基本概念

- 抽象类
(1)含有纯虚函数的类;
(2)抽象类不能用于直接创建对象实例,可以声明抽象类的指针和引用
(3)可使用指向抽象类的指针支持运行时多态性
(4)派生类中必须实现基类中的纯虚函数,否则它仍将被看作一个抽象类
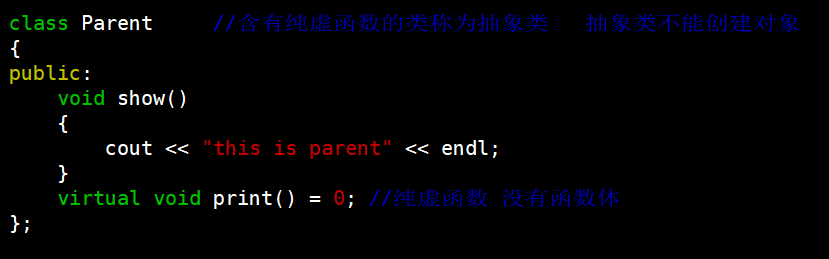
示例代码:
#include using namespace std;class Parent //含有纯虚函数的类称为抽象类 抽象类不能创建对象
{
public:void show(){cout << "this is parent" << endl;}virtual void print() = 0; //纯虚函数 没有函数体
};class Child : public Parent
{
public:void print(){cout << "this is Child" << endl;}
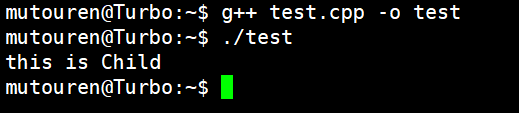
};int main()
{//Parent pp;//pp.print();Parent *p = new Child;p->print();return 0;
}
运行结果:
相关内容
热门资讯
保存时出现了1个错误,导致这篇...
当保存文章时出现错误时,可以通过以下步骤解决问题:查看错误信息:查看错误提示信息可以帮助我们了解具体...
汇川伺服电机位置控制模式参数配...
1. 基本控制参数设置 1)设置位置控制模式 2)绝对值位置线性模...
不能访问光猫的的管理页面
光猫是现代家庭宽带网络的重要组成部分,它可以提供高速稳定的网络连接。但是,有时候我们会遇到不能访问光...
不一致的条件格式
要解决不一致的条件格式问题,可以按照以下步骤进行:确定条件格式的规则:首先,需要明确条件格式的规则是...
本地主机上的图像未显示
问题描述:在本地主机上显示图像时,图像未能正常显示。解决方法:以下是一些可能的解决方法,具体取决于问...
表格列调整大小出现问题
问题描述:表格列调整大小出现问题,无法正常调整列宽。解决方法:检查表格的布局方式是否正确。确保表格使...
表格中数据未显示
当表格中的数据未显示时,可能是由于以下几个原因导致的:HTML代码问题:检查表格的HTML代码是否正...
Android|无法访问或保存...
这个问题可能是由于权限设置不正确导致的。您需要在应用程序清单文件中添加以下代码来请求适当的权限:此外...
【NI Multisim 14...
目录 序言 一、工具栏 🍊1.“标准”工具栏 🍊 2.视图工具...
银河麒麟V10SP1高级服务器...
银河麒麟高级服务器操作系统简介: 银河麒麟高级服务器操作系统V10是针对企业级关键业务...