「 Java 8 新特性 」Stream 中的 map、peek、foreach 方法的区别
「 Java 8 新特性 」Stream 中的 map、peek、foreach 方法的区别
文章参考:
面试官问:Stream 中的 map、peek、foreach 方法的区别?傻傻分不清楚。。
stream中的map,peek,foreach的区别
一、概述
在学习java 8的stream api时,我们会遇到map,peek以及foreach这三种不同的处理方法,到底它们之间有些什么样的区别呢?本篇文章讲为你揭晓。
Map
/*** Returns a stream consisting of the results of applying the given* function to the elements of this stream.** This is an intermediate* operation.** @param The element type of the new stream* @param mapper a non-interfering,* stateless* function to apply to each element* @return the new stream*/ Stream map(Function mapper);
总结一下,就是应用一个函数型的接口,返回一个新流,是一个中间操作。
peek
/*** Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, additionally* performing the provided action on each element as elements are consumed* from the resulting stream.** This is an intermediate* operation.**
For parallel stream pipelines, the action may be called at* whatever time and in whatever thread the element is made available by the* upstream operation. If the action modifies shared state,* it is responsible for providing the required synchronization.** @apiNote This method exists mainly to support debugging, where you want* to see the elements as they flow past a certain point in a pipeline:*
{@code* Stream.of("one", "two", "three", "four")* .filter(e -> e.length() > 3)* .peek(e -> System.out.println("Filtered value: " + e))* .map(String::toUpperCase)* .peek(e -> System.out.println("Mapped value: " + e))* .collect(Collectors.toList());* }** @param action a * non-interfering action to perform on the elements as* they are consumed from the stream* @return the new stream*/Stream peek(Consumer action);
总结一下:接收一个消费型(Consumer)的接口,是一个中间操作,主要是用于debug的,可以进行二次的流处理
ForEach
/*** Performs an action for each element of this stream.** This is a terminal* operation.**
The behavior of this operation is explicitly nondeterministic.* For parallel stream pipelines, this operation does not* guarantee to respect the encounter order of the stream, as doing so* would sacrifice the benefit of parallelism. For any given element, the* action may be performed at whatever time and in whatever thread the* library chooses. If the action accesses shared state, it is* responsible for providing the required synchronization.** @param action a * non-interfering action to perform on the elements*/void forEach(Consumer action);
总结一下,接收一个消费型的接口,然后无返回值,是一个终止操作,注意线程安全问题及集合遍历的顺序问题。
二、示例
我们先创建一个集合用于测试
private List languageList = new ArrayList() {{add("java");add("python");add("c++");add("php");add("go");
}};
peek 方法中的函数式接口参数不能有返回值:
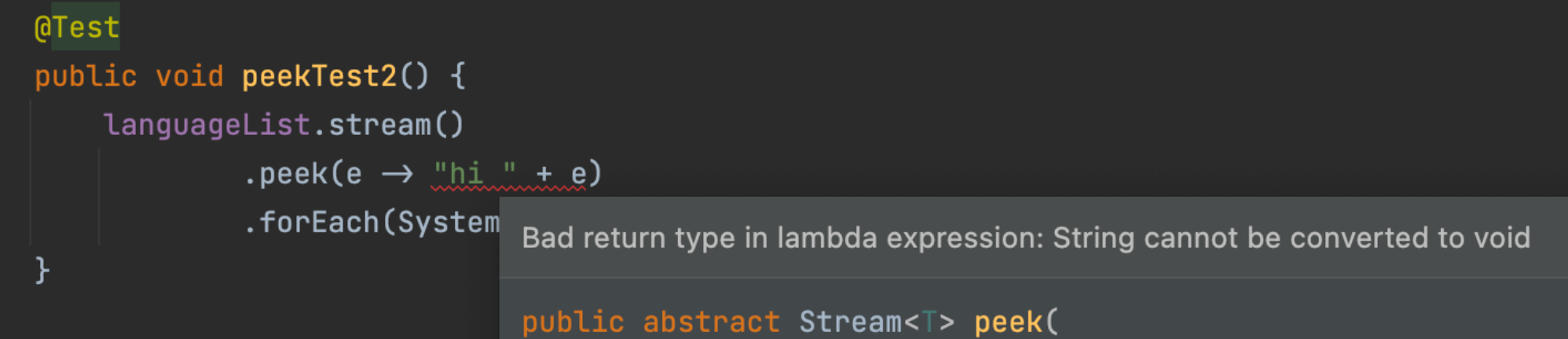
意味着它不能像 map 一样处理流中的元素然后形成新流:
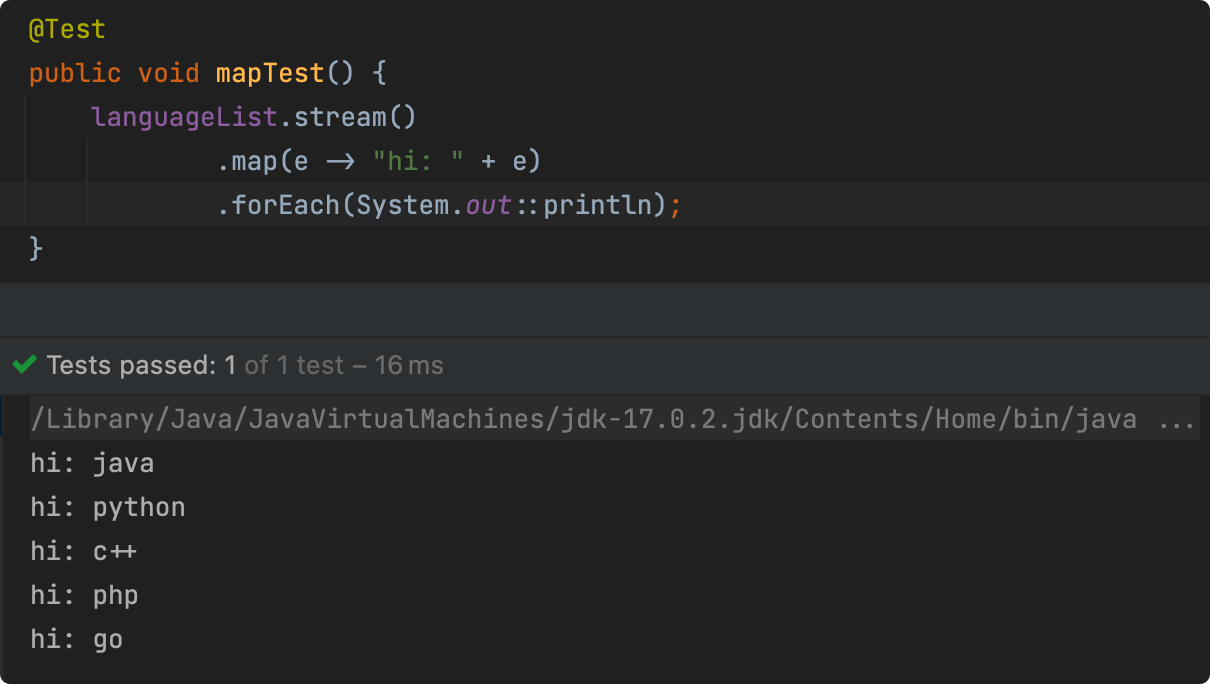
peek 不能修改流中的元素,只能对元素进行打印输出或者其他外部处理操作。
但流元素如果是引用类型,peek 却可以达到 map 的效果:
private List userList = new ArrayList() {{add(new User("张三"));add(new User("李四"));add(new User("王五"));add(new User("赵六"));
}};@Test
public void peekTest3() {userList.stream().peek(user -> user.setName("peek: " + user.getName())).forEach(System.out::println);
}
输出结果:
SteamPeekTest.User(name=peek: 张三)
SteamPeekTest.User(name=peek: 李四)
SteamPeekTest.User(name=peek: 王五)
SteamPeekTest.User(name=peek: 赵六)
虽然不能有返回值形成新的流,但却可以修改引用类型字段的值。
这也是建议的为什么要把 map 换成 peek 了,因为是引用类型,使用 peek 就没必要 set 之后还要进行 return 了。
List修改为:
List是不是优雅多了?
peek 和 foreach 有什么区别?
Foreach 和 peek 一样也是接收 Consumer 参数,不同是 foreach 没有返回参数,意味着 foreach 会中断流操作,只能用来遍历,不能再进行后续的流处理。
三、小结
根据文中的示例,大家应该都搞清楚了 map、peek、foreach 的区别和用法了,现在再来总结下吧!
- map:用于对流中的每个元素进行映射处理,然后再形成新的流;
- peek:用于 debug 调试流中间结果,不能形成新的流,但能修改引用类型字段的值;
- foreach:用于遍历,会中断流操作;
所以说,大家都搞清楚了吧?还有谁用错,把这篇文章发给他吧,让大家少走弯路,少写垃圾代码,共同进步。
上一篇:QT 常用控件类型命名参考