Linux串口应用编程
创始人
2025-05-29 02:38:50
0次
一、 串口API
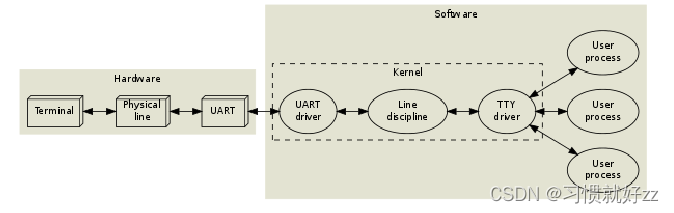
在Linux系统中,操作设备的统一接口就是:open/ioctl/read/write。
对于UART,又在ioctl之上封装了很多函数,主要是用来设置行规程。
所以对于UART,编程的套路就是:
- open
- 设置行规程,比如波特率、数据位、停止位、检验位、RAW模式、一有数据就返回
- read/write
怎么设置行规程?行规程的参数用结构体termios来表示,可以参考Linux串口—struct termios结构体
typedef unsigned char cc_t;
typedef unsigned int speed_t;
typedef unsgined int tcflag_t;#define NCCS 19
struct termios {tcflag_t c_iflag; /* input mode flags */tcflag_t c_oflag; /* output mode flags */tcflag_t c_cflag; /* control mode flags */tcflag_t c_lflag; /* local mode flags */cc_t c_line; /* line discipline */cc_t c_cc[NCCS]; /* control characters */
};
这些函数在名称上有一些惯例:
- tc: terminal control
- cf: control flag
| 函数名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| tcgetattr | get terminal attributes,获得终端的属性 |
| tcsetattr | set terminal attributes,修改终端参数 |
| tcflush | 清空终端未完成的输入/输出请求及数据 |
| cfsetispeed | sets the input baud rate,设置输入波特率 |
| cfsetospeed | sets the output baud rate,设置输出波特率 |
| cfsetspeed | 同时设置输入、输出波特率 |
函数不多,主要是需要设置好termios中的参数,这些参数很复杂,可以参考Linux串口—struct termios结构体。
二、编程
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include int set_opt(int fd, int nSpeed, int nBits, char nEvent, int nStop)
{struct termios newtio, oldtio;if(tcgetattr(fd, &oldtio) != 0) {perror("SetupSerial 1");return -1;}bzero(&newtio, sizeof(newtio));newtio.c_cflag |= CLOCAL|CREAD;newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE;newtio.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON|ECHO|ECHOE|ISIG);newtio.c_oflag &= ~OPOST;switch(nBits) {case 7:newtio.c_cflag |= CS7;break;case 8:newtio.c_cflag |= CS8;break;}switch(nEvent) {case 0:newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB;newtio.c_cflag |= PARODD;newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK | ISTRIP);break;case 'E':newtio.c_iflag |= (INPCK|ISTRIP);newtio.c_cflag |= PARENB;newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARODD;break;case 'N':newtio.c_cflag &= ~PARENB;break;}switch(nSpeed) {case 2400:cfsetispeed(&newtio, B2400);cfsetospeed(&newtio, B2400);break;case 4800:cfsetispeed(&newtio, B4800);cfsetospeed(&newtio, B4800);break;case 9600:cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600);cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600);break;case 115200:cfsetispeed(&newtio, B115200);cfsetospeed(&newtio, B115200);break;default:cfsetispeed(&newtio, B9600);cfsetospeed(&newtio, B9600);break;}if(nStop == 1)newtio.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB;else if(nStop == 2)newtio.c_cflag |= CSTOPB;newtio.c_cc[VMIN] = 1;newtio.c_cc[VTIME] = 0;tcflush(fd, TCIFLUSH);if((tcsetattr(fd, TCSANOW, &newtio)) != 0) {perror("com set error");return -1;}return 0;
}int open_port(char *com)
{int fd;fd = open(com, O_RDWR|O_NOCTTY);if(-1 == fd) {return -1;}if(fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, 0) < 0) {printf("fcntl failed\n");return -1;}return fd;
}int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{int fd;int iRet;char c;if(argc != 2) {printf("Usage: \n");printf("%s \n", argv[0]);return -1;}fd = open_port(argv[1]);if(fd < 0) {printf("open %s err!\n", argv[1]);return -1;}iRet = set_opt(fd, 115200, 8, 'N', 1);if(iRet) {printf("set port err!\n");return -1;}printf("Enter a char: ");while(1) {scanf("%c", &c);iRet = write(fd, &c, 1);iRet = read(fd, &c, 1);if(iRet == 1) {printf("get: %02x %c\n", c, c);} else {printf("can not get data\n");}}return 0;
}
三、上机实验
短接串口的RX和TX
root@npi:~/test# ./a.out /dev/ttymxc2
Enter a cahr: a
get: 61 a
get: 0a get: 0a get: 0a a
get: 61 a
get: 0a 相关内容
热门资讯
保存时出现了1个错误,导致这篇...
当保存文章时出现错误时,可以通过以下步骤解决问题:查看错误信息:查看错误提示信息可以帮助我们了解具体...
汇川伺服电机位置控制模式参数配...
1. 基本控制参数设置 1)设置位置控制模式 2)绝对值位置线性模...
不能访问光猫的的管理页面
光猫是现代家庭宽带网络的重要组成部分,它可以提供高速稳定的网络连接。但是,有时候我们会遇到不能访问光...
不一致的条件格式
要解决不一致的条件格式问题,可以按照以下步骤进行:确定条件格式的规则:首先,需要明确条件格式的规则是...
本地主机上的图像未显示
问题描述:在本地主机上显示图像时,图像未能正常显示。解决方法:以下是一些可能的解决方法,具体取决于问...
表格列调整大小出现问题
问题描述:表格列调整大小出现问题,无法正常调整列宽。解决方法:检查表格的布局方式是否正确。确保表格使...
表格中数据未显示
当表格中的数据未显示时,可能是由于以下几个原因导致的:HTML代码问题:检查表格的HTML代码是否正...
Android|无法访问或保存...
这个问题可能是由于权限设置不正确导致的。您需要在应用程序清单文件中添加以下代码来请求适当的权限:此外...
【NI Multisim 14...
目录 序言 一、工具栏 🍊1.“标准”工具栏 🍊 2.视图工具...
银河麒麟V10SP1高级服务器...
银河麒麟高级服务器操作系统简介: 银河麒麟高级服务器操作系统V10是针对企业级关键业务...