字符函数和字符串函数(上)-C语言详解
创始人
2025-05-29 14:20:17
0次
CSDN的各位友友们你们好,今天千泽为大家带来的是C语言中字符函数和字符串函数的详解,掌握了这些内容能够让我们更加灵活的运用字符串,
接下来让我们一起走进今天的内容吧!
写这篇文章需要在cplusplus.com上大量截图,十分不易!
如果对您有帮助的话希望能够得到您的支持和帮助,我会持续更新的!
0.前言
C语言中对字符和字符串的处理很是频繁,但是C语言本身是没有字符串类型的,字符串通常放在
常量字符串中或者字符数组中。
字符串常量适用于那些对它不做修改的字符串函数.
首先,我们将本次要介绍的函数分一下类
长度不受限制的字符串函数
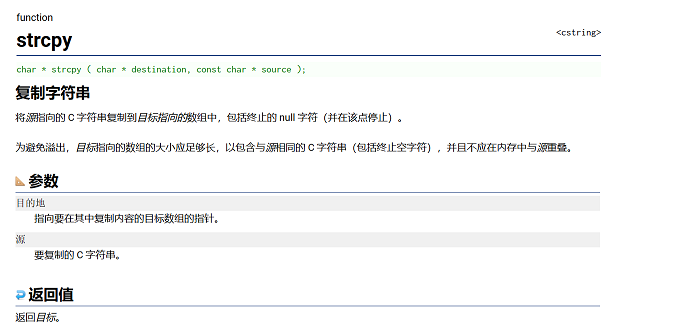
strcpy
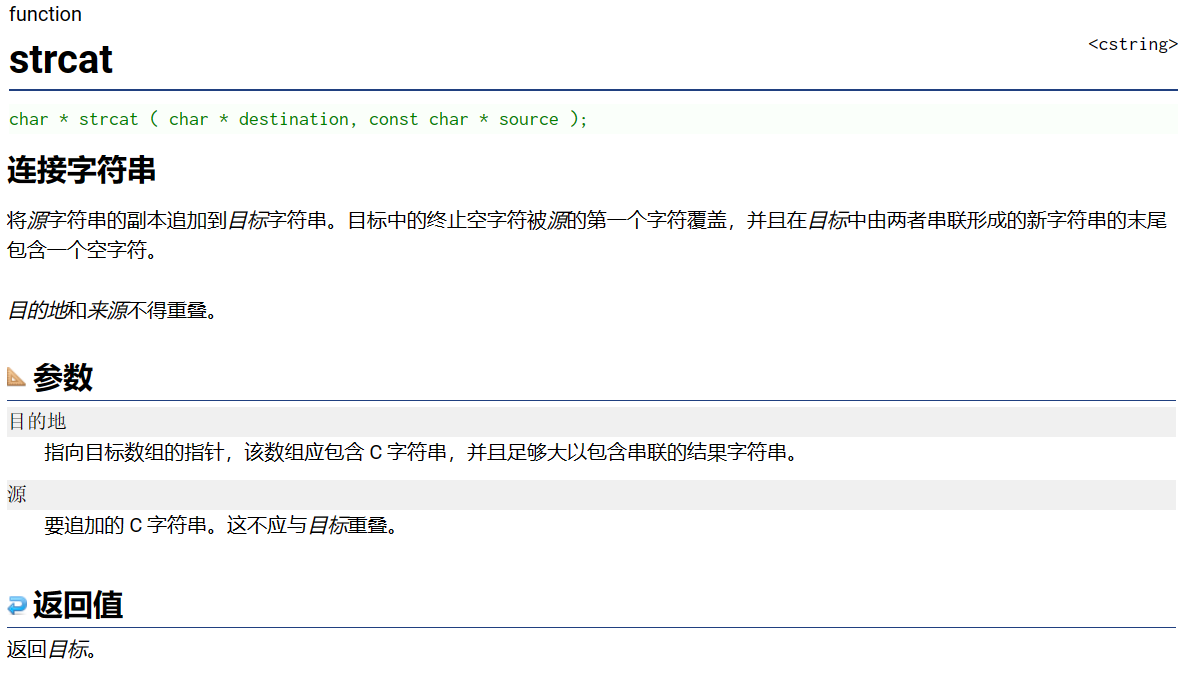
strcat
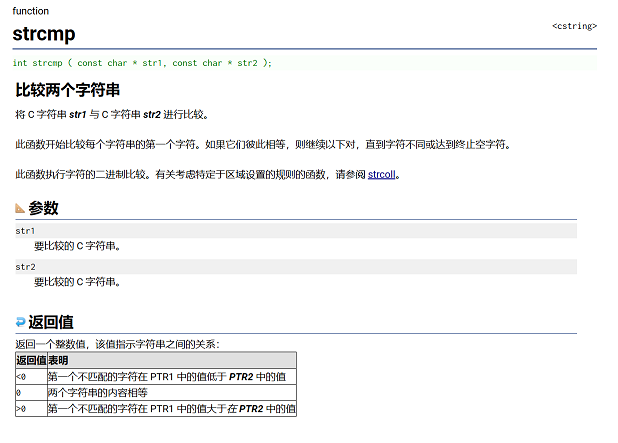
strcmp
长度受限制的字符串函数介绍
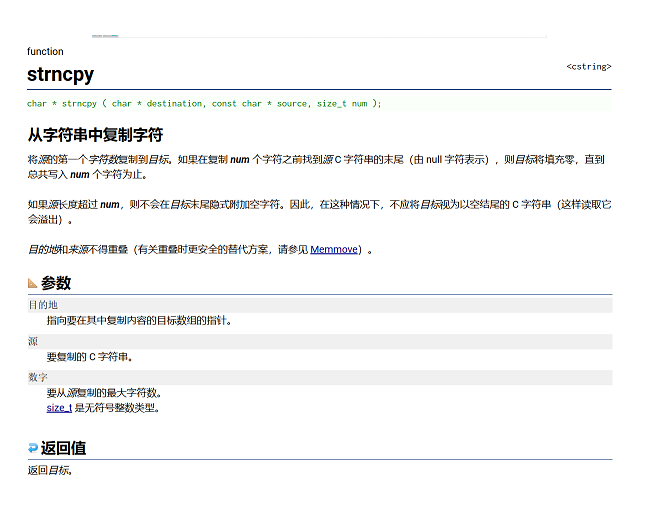
strncpy
strncat
strncmp
1.函数介绍
🚀strcpy
例子
/* strcpy example */
#include
#include int main ()
{char str1[]="Sample string";char str2[40];char str3[40];strcpy (str2,str1);strcpy (str3,"copy successful");printf ("str1: %s\nstr2: %s\nstr3: %s\n",str1,str2,str3);return 0;
} 输出:
str1: Sample string
str2: Sample string
str3: copy successful
🚩模拟实现strcpy
#include
#include
//1.参数顺序
//2.函数的功能,停止条件
//3.assert
//4.const修饰指针
//5.函数返回值
//6.题目出自《高质量C/C++编程》书籍最后的试题部分
//返回的是目标空间的起始地址
#include
char * my_strcpy(char * dest, const char* src)
{char * ret = dest;assert(dest!=NULL);assert(src != NULL);while ((*dest++ = *src++)){;}return ret;
}
int main()
{char arr1[] = "hehe";char arr2[20] = { 0 };my_strcpy(arr2, arr1);printf("%s\n", arr2);return 0;
} 友友们记得动手实践!!!
🚀strcat
官方例子
/* strcat example */
#include
#include int main ()
{char str[80];strcpy (str,"these ");strcat (str,"strings ");strcat (str,"are ");strcat (str,"concatenated.");puts (str);return 0;
} 输出
these strings are concatenated.
🚩模拟实现strcat
#include
#include
char* my_strcat(char* dest, const char* src)
{char* ret = dest;assert(dest != NULL);assert(src != NULL);//找目标空间的\0while (*dest!='\0'){dest++;}//拷贝while ((*dest++ = *src++)){;}return ret;
}
int main()
{char arr1[20] = "hello ";char arr2[] = "world";//追加my_strcat(arr1, arr2);printf("%s\n", arr1);return 0;
} 🚀strcmp
官方例子
#include
#include int main ()
{char key[] = "apple";char buffer[80];do {printf ("Guess my favorite fruit? ");fflush (stdout);scanf ("%79s",buffer);} while (strcmp (key,buffer) != 0);puts ("Correct answer!");return 0;
} 输出
Guess my favourite fruit? orange
Guess my favourite fruit? apple
Correct answer!
🚩模拟实现strcmp
#include
#include
#include
int my_strcmp(const char* str1, const char* str2)
{assert(str1 != NULL);assert(str2 != NULL);while (*str1 == *str2){if (*str1 == '\0'){return 0;}str1++;str2++;}if (*str1 > *str2){return 1;}else{return -1;}
}int main()
{char arr1[] = "abcdef";char arr2[] = "bbcdef";int ret = my_strcmp(arr1, arr2);printf("%d\n", ret);return 0;
} 🚀strncpy
官方例子
/* strncpy example */
#include
#include int main ()
{char str1[]= "To be or not to be";char str2[40];char str3[40];/* copy to sized buffer (overflow safe): */strncpy ( str2, str1, sizeof(str2) );/* partial copy (only 5 chars): */strncpy ( str3, str2, 5 );str3[5] = '\0'; /* null character manually added */puts (str1);puts (str2);puts (str3);return 0;
} 输出
To be or not to be To be or not to be To be
🚩模拟实现strncpy
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{char arr1[] = "abcdef";char arr2[5] = { 0 };strncpy(arr2, arr1, 3);printf("%s\n", arr2);return 0;
} 🚀strncat
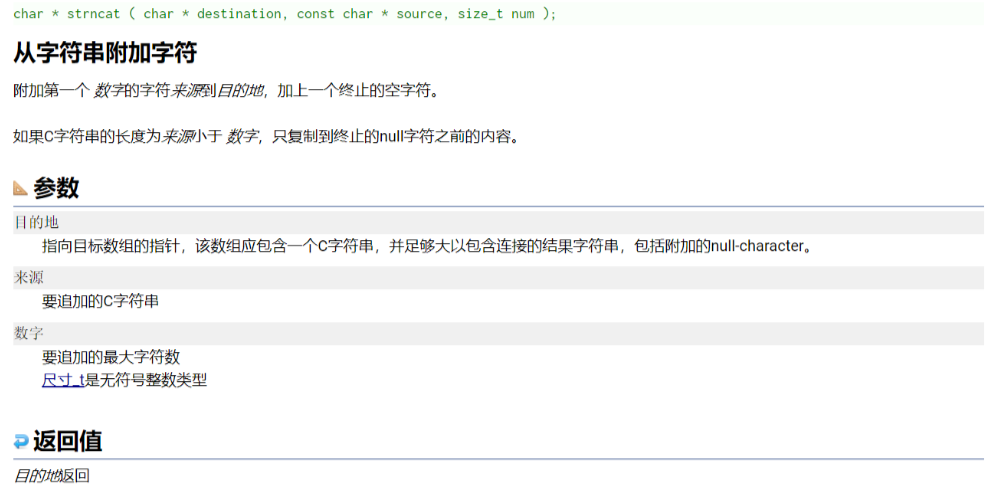
官方例子
/* strncat example */
#include
#include int main ()
{char str1[20];char str2[20];strcpy (str1,"To be ");strcpy (str2,"or not to be");strncat (str1, str2, 6);puts (str1);return 0;
} 输出
To be or not
🚩模拟实现strncat
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{char arr1[20] = "hello \0xxxxxxxx";char arr2[] = "world";strncat(arr1, arr2, 3);printf("%s\n", arr1);return 0;
} 🚀strncmp
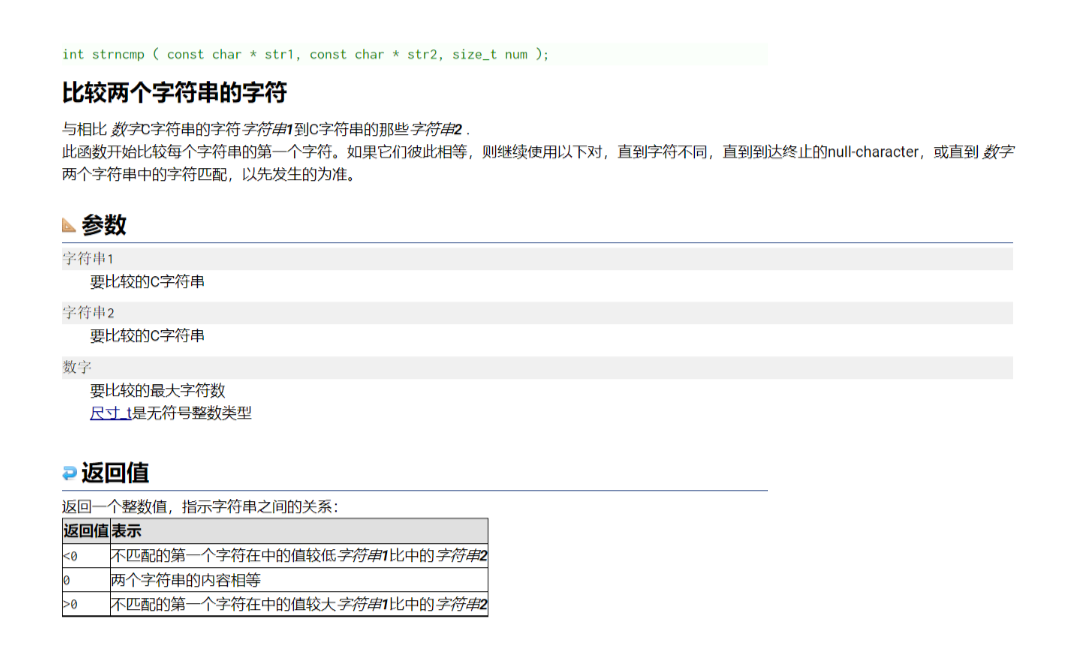
官方例子
/* strncmp example */
#include
#include int main ()
{char str[][5] = { "R2D2" , "C3PO" , "R2A6" };int n;puts ("Looking for R2 astromech droids...");for (n=0 ; n<3 ; n++)if (strncmp (str[n],"R2xx",2) == 0){printf ("found %s\n",str[n]);}return 0;
} 输出
Looking for R2 astromech droids... found R2D2 found R2A6
🚩模拟实现strncmp
#include
#include
#include
int main()
{char arr1[] = "abcdef";char arr2[] = "abcq";int ret = strncmp(arr1, arr2, 4);printf("%d\n", ret);return 0;
} 好了,今天的分享暂时告一段落,预知后续请看下篇😁,祝大家学习进步!

下一篇:百度将?百度已!
相关内容
热门资讯
保存时出现了1个错误,导致这篇...
当保存文章时出现错误时,可以通过以下步骤解决问题:查看错误信息:查看错误提示信息可以帮助我们了解具体...
汇川伺服电机位置控制模式参数配...
1. 基本控制参数设置 1)设置位置控制模式 2)绝对值位置线性模...
不能访问光猫的的管理页面
光猫是现代家庭宽带网络的重要组成部分,它可以提供高速稳定的网络连接。但是,有时候我们会遇到不能访问光...
不一致的条件格式
要解决不一致的条件格式问题,可以按照以下步骤进行:确定条件格式的规则:首先,需要明确条件格式的规则是...
本地主机上的图像未显示
问题描述:在本地主机上显示图像时,图像未能正常显示。解决方法:以下是一些可能的解决方法,具体取决于问...
表格列调整大小出现问题
问题描述:表格列调整大小出现问题,无法正常调整列宽。解决方法:检查表格的布局方式是否正确。确保表格使...
表格中数据未显示
当表格中的数据未显示时,可能是由于以下几个原因导致的:HTML代码问题:检查表格的HTML代码是否正...
Android|无法访问或保存...
这个问题可能是由于权限设置不正确导致的。您需要在应用程序清单文件中添加以下代码来请求适当的权限:此外...
【NI Multisim 14...
目录 序言 一、工具栏 🍊1.“标准”工具栏 🍊 2.视图工具...
银河麒麟V10SP1高级服务器...
银河麒麟高级服务器操作系统简介: 银河麒麟高级服务器操作系统V10是针对企业级关键业务...