Java多线程和多进程
线程 thread
任务task
多任务
举例子
一边吃饭一边玩手机
现实中太多这样同时做多件事情的例子了,看起来是多个任务都在做,其实本质上我们的大脑在同一时间依旧只做了一件事情。
多线程
一条路 和 多条道路

原来是一条路,慢慢因为车太多了,道路堵塞,效率极低。
为了提高使用的效率,能够充分利用道路,于是加了多个车道。
从此,妈妈再也不用担心道路堵塞了。
打游戏 用两个账号
普通方法调用 和 多线程
普通方法 多任务
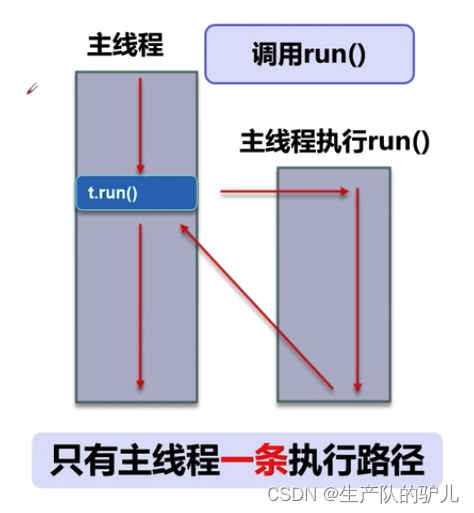
多线程
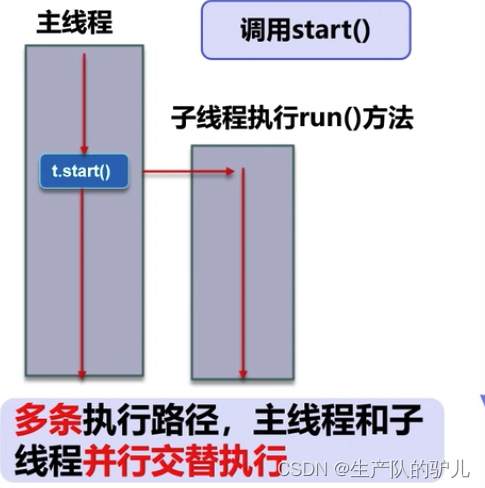
A process can have multiple threads
一个进程可以有多个线程,如视频中同时听声音,看图像,看弹幕,等等
程序是指令和数据的有序集合,其本身没有任何运行的含义,是静态的。
进程则是执行程序的一次执行过程, 动态概念。
一个进程 可以 包含 多个 线程。
一个进程中 至少 一个 线程。
线程是CPU调度和执行的的单位。
注意:很多多线程是模拟出来的,真正的多线程是指有多个cpu,即多核,如服务器。如果是模拟出来的多线程,即在一个cpu的情况下,在同一个时间点,cpu只能执行一个代码,因为切换的很快,所以就有同时执行的错局。
小节:
线程就是独立的执行路径;
在程序运行时,即使没有自己创建线程,后台也会有多个线程,如主线程,gc线程;
对同一份资源操作时,会存在资源抢夺的问题,需要加入并发控制;
在一个进程中,如果开辟了多个线程,线程的运行由调度器安排调度,调度器是与操作系统紧密相关的,先后顺序是不能认为的干预的。
线程会带来额外的开销,如cpu调度时间,并发控制开销。
每个线程在自己的工作内存交互,内存控制不当会造成数据不一致。
线程实现
一个程序 是静态的
执行起来就是 是 进程
一个 进程 里面 包含 多个线程
三种方式
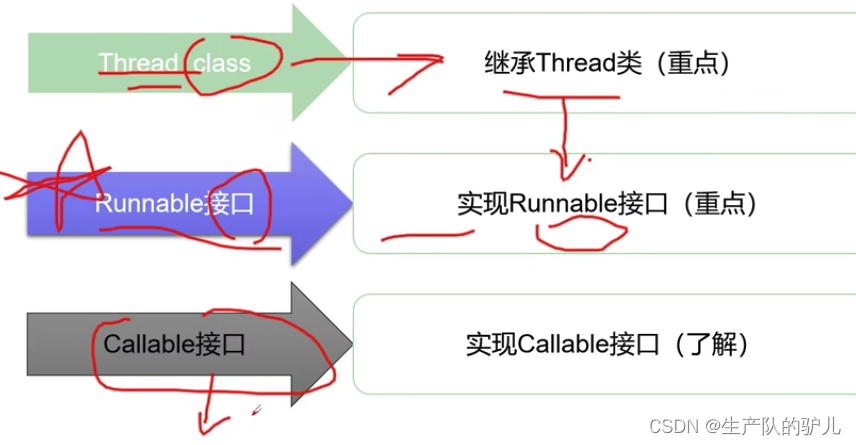
Thread类
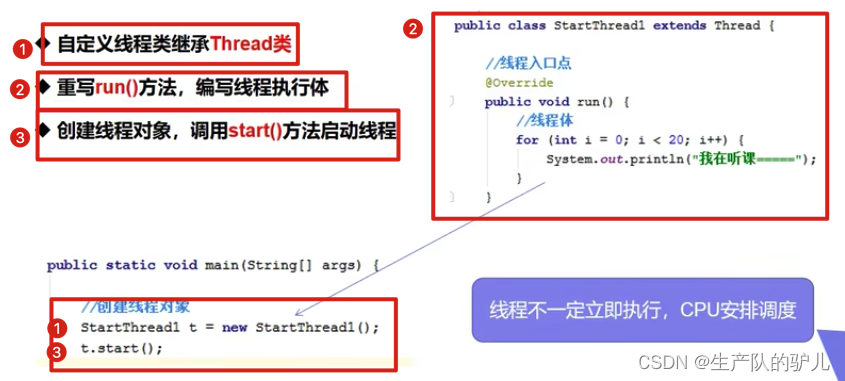
通过thread创建线程
public class Solution extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run() {// run 方法创建for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {System.out.println("test" + i);}}// main方法 是主线程public static void main(String[] args) {// 创建一个线程对象Solution test1 = new Solution();test1.start();// start方法 开启线程for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {System.out.println("i am testing " + i);}}
}
以下是运行结果
会发现
线程 和 进程 是同时 运行的。
注意: 线程开启 不一定立即执行
CPU调度 执行
test0
i am testing 0
test1
i am testing 1
test2
i am testing 2
test3
i am testing 3
test4
i am testing 4
test5
i am testing 5
test6
i am testing 6
i am testing 7
test7
i am testing 8
test8
i am testing 9
test9
i am testing 10
test10
i am testing 11
i am testing 12
i am testing 13
i am testing 14
i am testing 15
i am testing 16
i am testing 17
i am testing 18
i am testing 19
test11
test12
test13
test14
test15
test16
test17
test18
test19
例子2: 利用 多线程 同时 下载多个图片
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.io.File;
import java.net.URL;//实现多线程同步下载图片
public class TestThread2 extends Thread{private String url; // 网络图片地址private String name; // 保存的文件名public TestThread2(String url, String name) {this.url = url;this.name = name;}@Overridepublic void run(){WebDownLoader webDownLoader = new WebDownLoader();webDownLoader.download(url, name);System.out.println("下载了文件" + name);}public static void main(String[] args) {TestThread2 t1 = new TestThread2("https://kuangstudy.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/bbs/2021/08/03/kuangstudyaef93204-e2a6-41da-bf60-6a88e59da2b3.jpg","1.jpg");TestThread2 t2 = new TestThread2("https://kuangstudy.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/bbs/2021/08/03/kuangstudyaef93204-e2a6-41da-bf60-6a88e59da2b3.jpg","2.jpg");TestThread2 t3 = new TestThread2("https://kuangstudy.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/bbs/2021/08/03/kuangstudyaef93204-e2a6-41da-bf60-6a88e59da2b3.jpg","3.jpg");t1.start();t2.start();t3.start();}
}// 下载器
class WebDownLoader{// 下载方法public void download(String url, String name){try {FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(name));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("IO异常");throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
}
因为这几个图片是同时下载的,所以每次执行,下载的图片顺序是不一致的。
下载了文件1.jpg
下载了文件3.jpg
下载了文件2.jpg
如果没有io包
报错
去https://commons.apache.org/proper/commons-io/download_io.cgi
下载
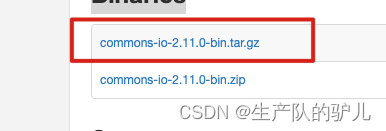
然后 解压
参考
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41425646/article/details/126510837?utm_medium=distribute.pc_relevant.none-task-blog-2defaultbaidujs_baidulandingword~default-0-126510837-blog-106325155.pc_relevant_aa2&spm=1001.2101.3001.4242.1&utm_relevant_index=3
Runnable接口
另一种方法来创建一个线程是声明实现类Runnable接口。那个类然后实现了run方法。然后可以分配类的实例,在创建Threat时作为传递,并启动。这种其他风格的同一个例子如下所示:


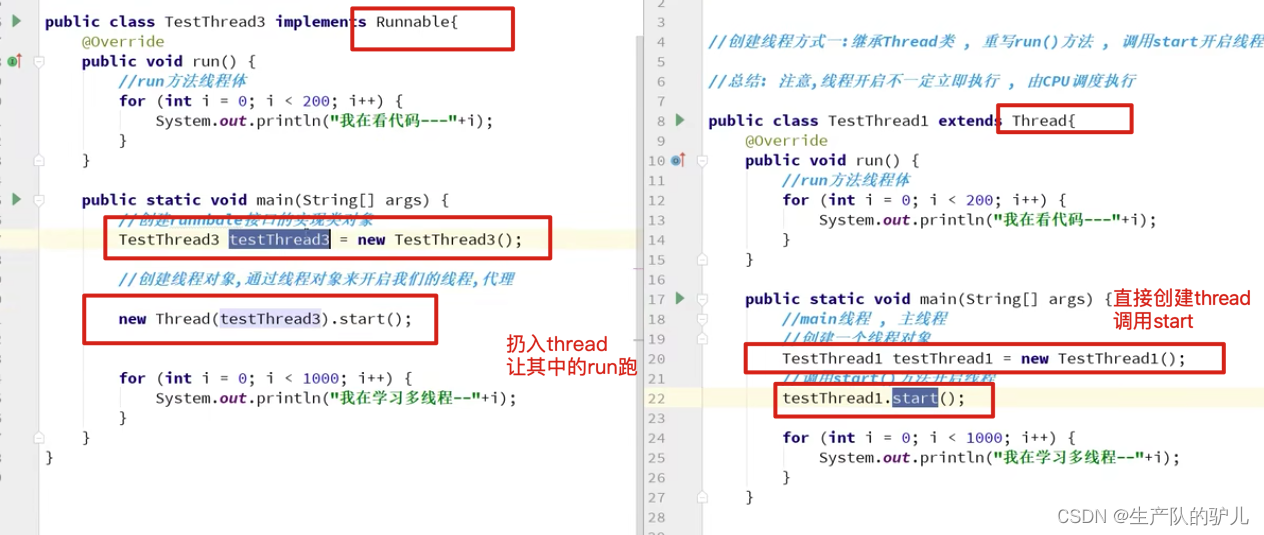
小节

runnable 例子
如果出现 多个线程thread 同时操作 同一个 对象
/*** 多个线程 同时 操作 同一个对象* 买火车票的 例子*/// 发现问题: 多个线程操作同一个资源
// 线程不安全
public class TestThread4 implements Runnable{private int ticketNum = 10;@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {if (ticketNum <= 0) break;try {Thread.sleep(200);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->拿到了第" + ticketNum-- + "票");}}public static void main(String[] args) {TestThread4 testThread4 = new TestThread4();new Thread(testThread4, "线程1").start();new Thread(testThread4,"线程2").start();new Thread(testThread4,"线程3").start();new Thread(testThread4,"线程3").start();}
}线程3--->拿到了第8票
线程3--->拿到了第7票
线程1--->拿到了第9票
线程2--->拿到了第10票
线程1--->拿到了第6票
线程3--->拿到了第6票
线程3--->拿到了第6票
线程2--->拿到了第6票
线程3--->拿到了第5票
线程2--->拿到了第5票
线程3--->拿到了第5票
线程1--->拿到了第5票
线程2--->拿到了第4票
线程3--->拿到了第3票
线程1--->拿到了第2票
线程3--->拿到了第4票
线程1--->拿到了第-1票
线程3--->拿到了第0票
线程3--->拿到了第-1票
线程2--->拿到了第1票
龟兔赛跑 Case
首先来个赛道距离,然后要离终点越来越近
判断比赛是否结束
打印出胜利者
龟兔赛跑开始
故事中是乌龟赢的,兔子需要睡觉,所以我们来模拟兔子睡觉,乌龟赢得比赛
public class Race implements Runnable{private static String winner;@Overridepublic void run(){for (int i = 0; i <= 100; i++) {if (Thread.currentThread().getName().equals("rabbit")) {try {Thread.sleep(1);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}boolean flag = gameOver(i);if (flag) break;System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->跑了" + i + "步");}}
// 判断比赛是否完成private boolean gameOver(int steps) {
// 判断是否有胜利者if (winner != null) { // 已经存在胜利者return true;}if (steps == 100) {winner = Thread.currentThread().getName();System.out.println("winner is " + winner);return true;}return false;}public static void main(String[] args) {Race race = new Race();new Thread(race, "rabbit").start();new Thread(race, "turtle").start();}
}Callable接口
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.concurrent.*;/*** callable的好处* 1. 可以定义返回值 Define return value* 2. 可以抛出异常 throw an exception.*/public class TestCallable implements Callable {private String url;private String name;public TestCallable(String url, String name) {this.url = url;this.name = name;}@Overridepublic Boolean call() {WebDownLoader2 webDownLoader2 = new WebDownLoader2();webDownLoader2.download(url, name);System.out.println("下载了文件名为: " + name);return true;}public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {TestCallable t1 = new TestCallable("https://kuangstudy.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/bbs/2021/08/03/kuangstudyaef93204-e2a6-41da-bf60-6a88e59da2b3.jpg","1.jpg");TestCallable t2 = new TestCallable("https://kuangstudy.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/bbs/2021/08/03/kuangstudyaef93204-e2a6-41da-bf60-6a88e59da2b3.jpg","2.jpg");TestCallable t3 = new TestCallable("https://kuangstudy.oss-cn-beijing.aliyuncs.com/bbs/2021/08/03/kuangstudyaef93204-e2a6-41da-bf60-6a88e59da2b3.jpg","3.jpg");// 创建执行服务// Create Execution ServiceExecutorService ser = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(3);// 提交执行// Submit for executionFuture r1 = ser.submit(t1);Future r2 = ser.submit(t2);Future r3 = ser.submit(t3);// 获取结果// Get the resultsboolean rs1 = r1.get();boolean rs2 = r2.get();boolean rs3 = r3.get();// 关闭服务// Shut down serviceser.shutdownNow();}
}class WebDownLoader2{// 下载方法public void download(String url, String name){try {FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url), new File(name));} catch (IOException e) {e.printStackTrace();System.out.println("IO异常");throw new RuntimeException(e);}}
} Lamda表达式
样子

函数式接口
functional interface
任何接口, 如果 只包含唯一 一个抽象方法
它就是 函数式 接口。
public interface Runnable {public abstract void run();
}
public class TestLambda2 {
// static class Love implements ILove {
// @Override
// public void love(int a) {
// System.out.println("I Love You ---> " + a);
// }
// }public static void main(String[] args) {// class Love implements ILove{
// @Override
// public void love(int a) {
// System.out.println("I Love You ---> " + a);
// }
// }// ILove love = new ILove() {
// @Override
// public void love(int a) {
// System.out.println("I Love You ---> " + a);
// }
// };// ILove love = (int a) -> {
// System.out.println("I Love You ---> " + a);
// };// 简化 参数类型
// ILove love = (a) -> {
// System.out.println("I Love You ---> " + a);
// };// 简化 括号ILove love = a -> {System.out.println("I Love You ---> " + a);};// 去掉花括号ILove iLove = a -> System.out.println("I Love You ---> " + a);/*** 总结* 能去掉 花括号的愿意是因为 这个代码只有一行* 多个参数 也得加 括号*/love.love(520);}
}interface ILove{void love(int a);
}静态代理模式
如何理解 代理
以结婚 作为例子 理解 代理:

/**** 静态代理模式总结:* 真实对象 和 代理对象 都要实现 同一个接口* 代理对象 要 代理 真是角色** 好处:* 代理对象可以做很多真实对象做不了的事情* 真实对象专注做自己的事情** 实际应用:* Thread线程中, 创建 Runnable** 线程开启* new Thread(new Runnable) {* @Override* public void run() {** }.start();* }** lambda 表达式 简化** new Thread( () -> System.out.println("我爱你") ).start();* WeddingCompany weddingCompany = new WeddingCompany(new You());*/public class StaticProxy {public static void main(String[] args) {// new 一个真实对象You you = new You();WeddingCompany weddingCompany = new WeddingCompany(you);weddingCompany.HappyMarry();}
}interface Marry{void HappyMarry();
}// 真实角色,你去结婚
class You implements Marry{@Overridepublic void HappyMarry() {System.out.println("xxx要结婚");}
}// 代理角色,帮助你结婚
class WeddingCompany implements Marry{// 代理谁 ---> 真实目标角色private Marry target;public WeddingCompany(Marry target) {this.target = target;}@Overridepublic void HappyMarry() {before();this.target.HappyMarry();after();}private void after(){System.out.println("结婚前,布置现场");}private void before(){System.out.println("结婚后,收尾款");}
}
线程状态
线程五大状态:
创建,就绪,阻塞,运行,死亡
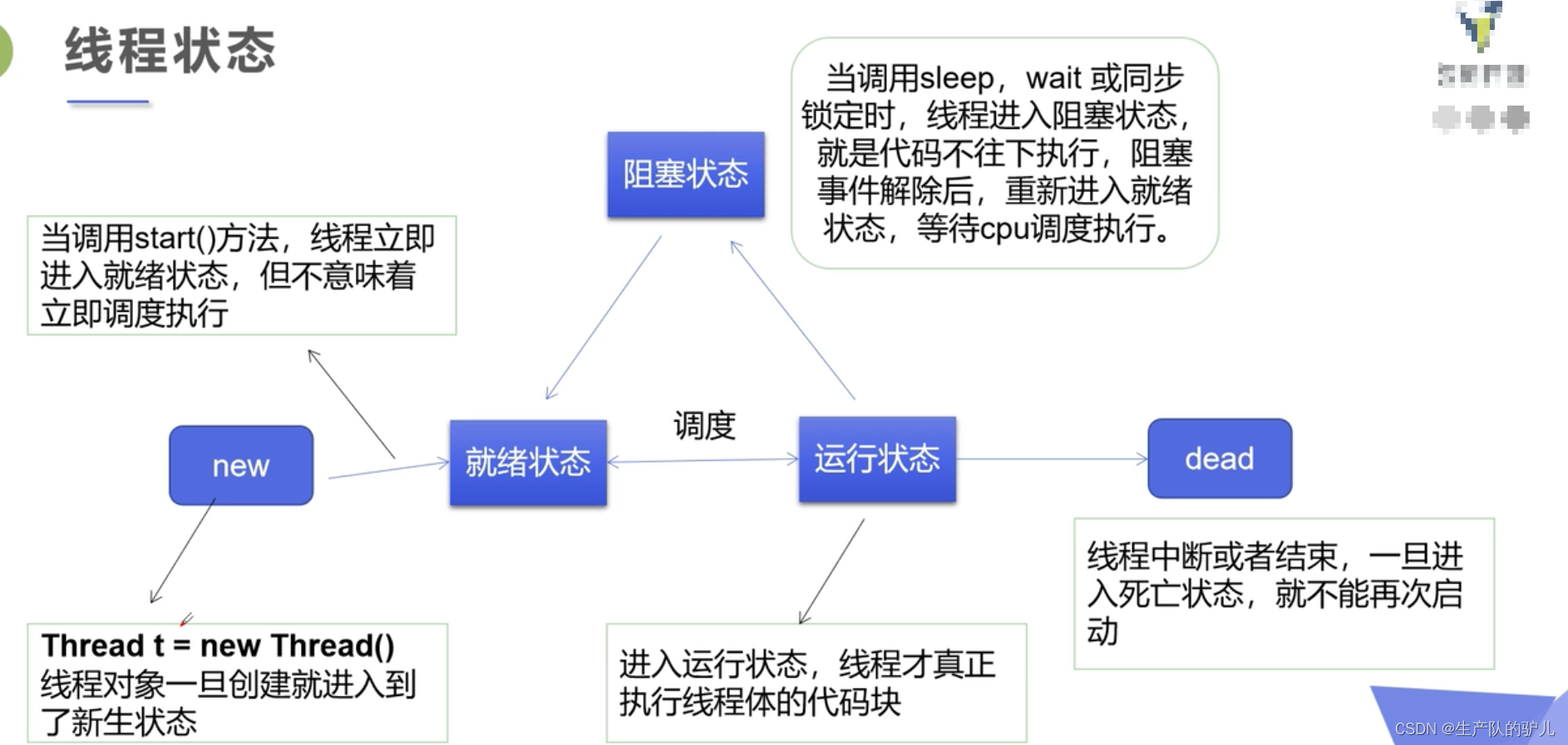
线程方法:
setPriority(int newPriority) 更改线程的优先级
static void sleep(long millis) 在指定的毫秒数内让当前正在执行的线程休眠
void join() 等待该线程终止
static void yield()
暂停当前正在执行的线程对象,并执行其他线程
void interrrupt()
中断线程,别用这个方法
boolean isAlive()
测试简称是否处于活动状态
停止线程

例子
/*** 测试 stop* 1. 建议线程正常停止 --> 利用次数,不建议死循环* 2. 建议使用标志位* 3. 不建议使用 stop 和 destory method*/public class TestStop implements Runnable{private boolean flag = true;@Overridepublic void run() {int i = 0;while (flag) {System.out.println("run thread + " + i++);}}public void stop(){this.flag = false;}public static void main(String[] args) {TestStop testStop = new TestStop();new Thread(testStop).start();for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {System.out.println("main" + i);if (i == 90) {// 调用stop切换标志位// 线程停止testStop.stop();System.out.println("线程该停止了");}}}
}/Library/Java/JavaVirtualMachines/jdk-11.0.16.jdk/Contents/Home/bin/java -javaagent:/Applications/IntelliJ IDEA.app/Contents/lib/idea_rt.jar=57251:/Applications/IntelliJ IDEA.app/Contents/bin -Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 -classpath /Users/zhouzhenzhou/Desktop/java-thread-/out/production/java-thread-:/Users/zhouzhenzhou/Desktop/java-thread-/libs/commons-io-2.11.0.jar TestStop
run thread + 0
main0
run thread + 1
main1
run thread + 2
main2
main3
run thread + 3
main4
run thread + 4
main5
run thread + 5
main6
run thread + 6
main7
run thread + 7
main8
run thread + 8
main9
main10
run thread + 9
main11
main12
main13
main14
main15
main16
run thread + 10
main17
run thread + 11
main18
main19
run thread + 12
main20
run thread + 13
main21
run thread + 14
main22
run thread + 15
main23
run thread + 16
main24
run thread + 17
main25
run thread + 18
main26
run thread + 19
main27
run thread + 20
main28
run thread + 21
main29
run thread + 22
main30
run thread + 23
run thread + 24
run thread + 25
run thread + 26
run thread + 27
run thread + 28
run thread + 29
main31
run thread + 30
run thread + 31
main32
run thread + 32
main33
run thread + 33
main34
run thread + 34
main35
run thread + 35
main36
run thread + 36
main37
run thread + 37
main38
run thread + 38
main39
run thread + 39
main40
run thread + 40
main41
run thread + 41
main42
run thread + 42
main43
run thread + 43
main44
run thread + 44
main45
run thread + 45
main46
run thread + 46
main47
run thread + 47
run thread + 48
main48
run thread + 49
main49
run thread + 50
main50
main51
run thread + 51
main52
run thread + 52
run thread + 53
run thread + 54
run thread + 55
main53
run thread + 56
main54
run thread + 57
main55
run thread + 58
main56
run thread + 59
main57
run thread + 60
main58
main59
main60
main61
run thread + 61
main62
run thread + 62
main63
main64
main65
main66
main67
main68
main69
main70
main71
main72
main73
main74
main75
main76
main77
main78
main79
main80
main81
main82
main83
main84
main85
run thread + 63
run thread + 64
run thread + 65
run thread + 66
run thread + 67
run thread + 68
run thread + 69
run thread + 70
run thread + 71
run thread + 72
run thread + 73
run thread + 74
run thread + 75
run thread + 76
run thread + 77
main86
run thread + 78
run thread + 79
run thread + 80
run thread + 81
run thread + 82
run thread + 83
run thread + 84
run thread + 85
run thread + 86
run thread + 87
run thread + 88
run thread + 89
run thread + 90
run thread + 91
run thread + 92
run thread + 93
main87
run thread + 94
main88
run thread + 95
main89
run thread + 96
main90
run thread + 97
线程该停止了
main91
main92
main93
main94
main95
main96
main97
main98
main99Process finished with exit code 0线程休眠

模拟网络延时
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;/*** 网络延时 会导致 多个线程 操作同一个对象** 线程休眠 可以 模拟 网络延时***/public class TestSleep {public static void tenDown() throws InterruptedException {int num = 10;while (true) {Thread.sleep(1000);System.out.println(num--);if (num <= 0) {break;}}}public static void main(String[] args) {// 打印当前系统时间Date startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); // 获取系统当前时间while (true) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);// 获取系统当前时间System.out.println(new SimpleDateFormat("HH:mm:ss").format(startTime));startTime = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis()); // 跟新系统当前时间} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}
// tenDown();}
}
sleep 时间 指定当前线程 阻塞的毫秒数;
sleep 存在异常InterrruptedException;
sleep 时间达到后线程进入就绪状态;
sleep 可以模拟网络延时,倒计时等。
每一个对象 都有一个锁, sleep 不会释放锁。
线程礼让
礼让线程,让当前正在执行的线程暂停,但不阻塞
将线程从运行状态转为就绪状态
Transition a thread from a running state to a ready state
让cpu重新调度,礼让不一定成功!看CPU心情
/*** 测试礼让线程**/
public class TestYield {public static void main(String[] args) {MyYield myYield = new MyYield();new Thread(myYield, "a").start();new Thread(myYield, "b").start();}
}class MyYield implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程开始执行");Thread.yield(); // 礼让System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "线程停止执行");}
}
a线程开始执行
b线程开始执行
a线程停止执行
b线程停止执行
Join 合并线程
Join合并线程,待此线程执行完成后,再执行其他线程,其他线程阻塞。
可以 理解为 插队
/*** 测试join方法* 想象为插队*/
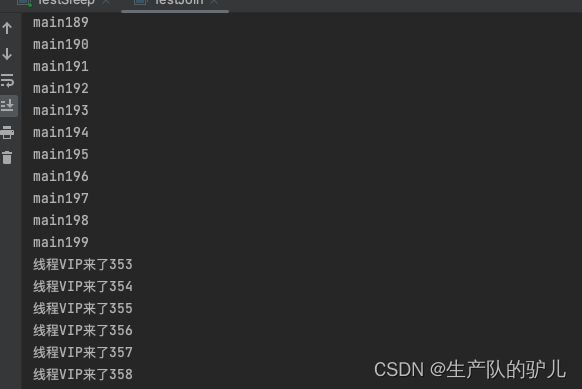
public class TestJoin implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {System.out.println("线程VIP来了" + i);}}public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {TestJoin testJoin = new TestJoin();Thread thread = new Thread(testJoin);thread.start();// 主线程for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {if (i == 200) {thread.join(); // 线程到200的时候,直接插队}System.out.println("main" + i );}}
}
小节回顾 线程的五个状态

线程状态观测
public class TestState {public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {Thread thread = new Thread(() -> {for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}System.out.println("/");});// 观察状态Thread.State state = thread.getState();System.out.println(state); // NEw// 观察启动后thread.start(); // 启动线程state = thread.getState();System.out.println(state);while (state != Thread.State.TERMINATED) {// 只要线程不终止,就一直输出状态Thread.sleep(1000);state = thread.getState();System.out.println(state);}thread.start(); // error: 线程一旦死亡,就不能再启动}
}线程优先级
Java提供一个线程调度器来监控程序中启动后进入就绪状态的所有线程,线程调度器按照优先级决定应该调度哪个线程来执行。
线程的优先级用数字表示,范围从1~10 Thread。
MIN_PRIORITY = 1;
Thread.MAX_ PRIORITY = 10;
Thread.NORM_PRIORITY = 5;
优先级低只是意味着获得调度的概率低。并不是优先级低就不会被调用了。这都是看CPU的调度
public class TestPriority {public static void main(String[] args) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "-->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());MyPriority myPriority = new MyPriority();Thread t1 = new Thread(myPriority);Thread t2 = new Thread(myPriority);Thread t3 = new Thread(myPriority);Thread t4 = new Thread(myPriority);Thread t5 = new Thread(myPriority);Thread t6 = new Thread(myPriority);// 先设置优先级再启动t1.start();t2.setPriority(1);t2.start();t3.setPriority(4);t3.start();t4.setPriority(Thread.MAX_PRIORITY); // 10t4.start();
// 会报错error 因为 优先级 0 - 10
// t5.setPriority(-1);
// t5.start();// t6.setPriority(11);
// t6.start();}
}class MyPriority implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "--->" + Thread.currentThread().getPriority());}
}守护线程
daemon 线程
线程分为用户线程和守护线程
虚拟机必须确保用户线程执行完毕
虚拟机不用等待守护线程执行完毕
如,后台记录操作日志,监控内存,垃圾回收等待。
/*** 测试 守护线程* 上帝守护你*/
public class TestDaemon {public static void main(String[] args) {God god = new God();You1 you = new You1();Thread thread = new Thread(god);thread.setDaemon(true); // 默认是false,表示是用户线程thread.start();// 上帝守护线程启动new Thread(you).start();}}class God implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {System.out.println("上帝保佑着你");}}
}// 你
class You1 implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {
// for(int i = 0; i < 36500000; i++) {for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {System.out.println("你一生都开心的活着");}System.out.println("-====goodbye! world!");}
}线程同步
多个线程 操作 同一个 资源
并发
同一个对象被 多个线程同时操作

线程同步
排队
处理多线程问题时,多个线程访问同一个对象,并且某些线程还想修改这个对象. 这时候我们就需要线程同步。线程同步其实就是一种等待机制,多个需要同时访问此对象的线程进入这个对象的等待池形成队列,等待前面线程使用完毕,下一个线程再使用

队列 和 锁
锁 可以 理解为
上厕所时候,要锁上门,不然别人就进去了。

线程不安全的三个例子
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.util.TreeMap;/*** 线程不安全: ----> 有负数***/public class unsafeBuyTicket {public static void main(String[] args) {BuyTicket station = new BuyTicket();new Thread(station, "我").start();new Thread(station,"你们").start();new Thread(station, "黄牛").start();}
}class BuyTicket implements Runnable{private int ticketNums = 10;boolean flag = true; // 外部停止方式@Overridepublic void run() {// buy ticketwhile (flag) {try {buy();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}private void buy() throws InterruptedException {// 判断是否有票if (ticketNums <= 0) {return;}// 模拟延时Thread.sleep(100);// 买票System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿到" + ticketNums--);}
}
/*** 不安全的取钱* 两个人去银行取钱,账户*/public class UnsafeBank {public static void main(String[] args) {// 账户Account account = new Account(100,"结婚基金");Drawing you = new Drawing(account, 50, "你");Drawing girlFriend = new Drawing(account, 100, "GirlFriend");you.start();girlFriend.start();}
}// 账户
class Account {int money;String name;public Account(int money, String name) {this.money = money;this.name = name;}
}// 银行: 模拟取款
class Drawing extends Thread {Account account; // 账户 account// 取了多少钱 How much did you withdrawint drawingMoney;// 现在手里钱 Now the money in handint nowMoney;public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney, String name) {super(name);this.account = account;this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney;}@Overridepublic void run(){// 判断有没有钱if (account.money - drawingMoney < 0) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "钱不够,取不了");return;}try {Thread.sleep(10000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}// 卡内余额 = 余额 - 你的钱account.money = account.money - drawingMoney;nowMoney = nowMoney + drawingMoney;System.out.println(account.name + "余额为:" + account.money);// Thread.currentThread().getName() 和 this.getName() 等价System.out.println(this.getName() + "手里的钱:" + nowMoney);}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;/*** 线程不安全的集合* A collection of unsafe threads* 但是为什么会出现没到10000的情况呢 就是main线程睡眠到醒过来的时间list添加还是没有结束*/public class UnsafeList {public static void main(String[] args) {List list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {new Thread(()-> {list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());}).start();}try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println(list.size());}
}
// 结果 size 少于 100000, 因为有些线程之间 同时重复覆盖了,导致size不够
// As a result, the size is less than 100000,
// because some threads are repeatedly covered at the same time,
// resulting in insufficient size.
线程同步
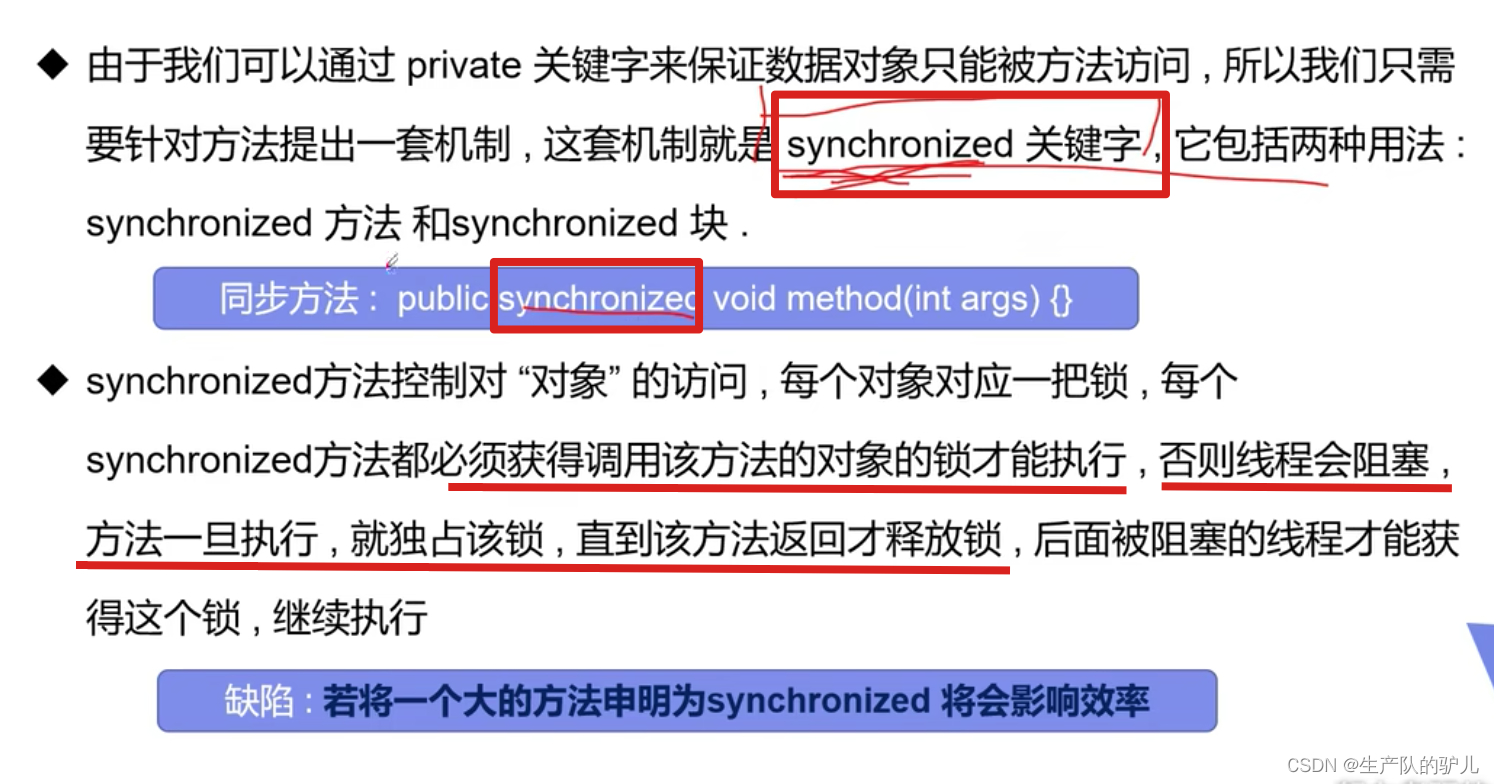
同步缺陷
方法里面需要修改的内容才需要锁, 锁的太多,浪费资源
修改 上面不安全线程为安全线程
1.在buy()加synchronized出现只有第一个拿走了全部的票
2.且输出结果出现了-1,是因为第一个线程执行buy()时sleep了
3.此时buy()的锁并没有释放,但run()并没有锁,其他两个线程卡在了buy()前
5.票为0时,第一个线程的while()结束,剩下两个线程执行一遍run()后结束
6.修改方法:将buy()中的sleep()移到run()中的buy()后面应该是里面外面都要sleep一下,外面sleep可以让别人抢到票,里面sleep可以模拟抢票延迟第一个线程进去后锁住了对象,锁外不加sleep会一直跑这个线程
import java.nio.ByteBuffer;
import java.util.TreeMap;/*** 线程不安全: ----> 有负数***/public class unsafeBuyTicket {public static void main(String[] args) {BuyTicket station = new BuyTicket();new Thread(station, "我").start();new Thread(station,"你们").start();new Thread(station, "黄牛").start();}
}class BuyTicket implements Runnable{private int ticketNums = 10;boolean flag = true; // 外部停止方式@Overridepublic void run() {// buy ticketwhile (flag) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);buy();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}// private void buy() throws InterruptedException { // 不安全线程// 同步方法
// 锁的是thisprivate synchronized void buy() throws InterruptedException { // 修改为安全线程// 判断是否有票if (ticketNums <= 0) {flag = false;return;}// 模拟延时
// Thread.sleep(100000);// 买票System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "拿到" + ticketNums--);}
}

修改 银行账户
他这里说的锁银行而不是锁this 指的是当前类 也就是银行的class Drawing.class而synchronized方法 想让锁对象是当前类的class ,要么只能有一个银行的实例对象, 要么ynchronized方法前用static修饰 这样也能保证锁对象是类的class而他有两个银行的实例对象 you 和girlfriend 两个实例对象 那么这两个实例对象开启了两条线程,每条线程用的锁对象都是当前实例对象 锁对象不同是无法实现同步的。最简单的方法就是 用synchronized代码块 在synchronized(){}, 小括号中放当前类的class,因为一个类是只能有一个class的 所以 能保证锁对象是一样的 而实现同步
ps:小括号中只要是一个唯一的就行 对象 class都可以 其实只要记住下面这三点 任何时候都不会搞错同步方法或同步代码块中的锁对象是什么了
对于普通同步方法,锁是当前实例对象。 如果有多个实例 那么锁对象必然不同无法实现同步。
对于静态同步方法,锁是当前类的Class对象。有多个实例 但是锁对象是相同的 可以完成同步。
对于同步方法块,锁是Synchonized括号里配置的对象。对象最好是只有一个的 如当前类的 class 是只有一个的 锁对象相同 也能实现同步。
其实只要记住下面这三点
任何时候都不会搞错同步方法或同步代码块中的锁对象是什么。
对于普通同步方法,锁是当前实例对象。
如果有多个实例 那么锁对象必然不同无法实现同步。
对于静态同步方法,锁是当前类的Class对象。有多个实例 但是锁对象是相同的 可以完成同步。
小节
简而言之,如果资源在同一个类中,就用同步方法;如果不在同一个类中,就用同步块。
In short, if the resources are in the same class, use the synchronization method; If not in the same class, use synchronous blocks.
/*** 不安全的取钱* 两个人去银行取钱,账户*/public class UnsafeBank {public static void main(String[] args) {// 账户Account account = new Account(100,"结婚基金");Drawing you = new Drawing(account, 50, "你");Drawing girlFriend = new Drawing(account, 100, "GirlFriend");you.start();girlFriend.start();}
}// 账户
class Account {int money;String name;public Account(int money, String name) {this.money = money;this.name = name;}
}// 银行: 模拟取款
class Drawing extends Thread {Account account; // 账户 account// 取了多少钱 How much did you withdrawint drawingMoney;// 现在手里钱 Now the money in handint nowMoney;public Drawing(Account account, int drawingMoney, String name) {super(name);this.account = account;this.drawingMoney = drawingMoney;}@Override
// public void run(){public void run(){// 这里的account都是主函数传过来的结婚基金的account对象实例,是同一个/*** 其实这里同步只能按方法去锁对象,* 但是这里具体操作Drawing类的取钱方法的是new的两个账户,* 我们要锁的是两个不同的对象,所以单纯在方法里加syn锁不到两个对象,所以用同步块*/synchronized (account) {// 判断有没有钱if (account.money - drawingMoney < 0) {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "钱不够,取不了");return;}try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}// 卡内余额 = 余额 - 你的钱account.money = account.money - drawingMoney;nowMoney = nowMoney + drawingMoney;System.out.println(account.name + "余额为:" + account.money);// Thread.currentThread().getName() 和 this.getName() 等价System.out.println(this.getName() + "手里的钱:" + nowMoney);}}
}
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;/*** 线程不安全的集合* A collection of unsafe threads* 但是为什么会出现没到10000的情况呢 就是main线程睡眠到醒过来的时间list添加还是没有结束*/public class UnsafeList {public static void main(String[] args) {List list = new ArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {new Thread(()-> {synchronized (list) { // 上锁,修改为安全线程list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());}}).start();}try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println(list.size());}
}
// 结果 size 少于 100000, 因为有些线程之间 同时重复覆盖了,导致size不够
// As a result, the size is less than 100000,
// because some threads are repeatedly covered at the same time,
// resulting in insufficient size. GUC安全进程测试
import java.util.concurrent.CopyOnWriteArrayList;/*** 测试GUC 安全类型集合*/
public class TesyGUC {public static void main(String[] args) {CopyOnWriteArrayList list = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {new Thread(() -> {list.add(Thread.currentThread().getName());}).start();}try {Thread.sleep(3000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println(list.size());}
} 死锁 DeadLock
多个线程各自占有一些共享资源,并且互相等待其他线程占有的资源才能运行,而导致两个或者多个线程都在等待对方释放资源,都停止执行的情形。某一个同步块同时拥有“两个以上对象的锁”时,就可能会发生“死锁”的问题.
/*** 死锁:多个线程互相热着对方需要内资源,然后形成僵持。*/
public class DeadLock {public static void main(String[] args) {Makeup g1 = new Makeup("灰姑凉",0);Makeup g2 = new Makeup("白雪公主",1);g1.start();g2.start();}
}class LipStick{
}
class Mirror{
}
class Makeup extends Thread {// static 保证资源只有一份static LipStick lipStick = new LipStick();static Mirror mirror = new Mirror();int choice; // 选择String name; // 使用化妆品的人Makeup(String name, int choice) {this.name = name;this.choice = choice;}@Overridepublic void run(){super.run();try {makeup();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}private void makeup() throws InterruptedException {if (choice == 0) {synchronized (lipStick) {System.out.println(this.name + "获得口红的锁");Thread.sleep(1000);synchronized (mirror) {System.out.println(this.name + "获得镜子的锁");}}}else {synchronized (mirror) {System.out.println(this.name + "获得镜子的锁");Thread.sleep(2000);synchronized (lipStick) {System.out.println(this.name + "获得口红的锁");}}}}
}如何避免死锁
产生死锁的四个必要条件:1. 互斥条件:一个资源每次只能被一个进程使用。2. 请求与保持条件:一个进程因请求资源而阻塞时,对已获得的资源保持不放。3.不剥夺条件:进程已获得的资源,在末使用完之前,不能强行剥夺。4. 循环等待条件:若干进程之间形成一种头尾相接的循环等待资源关系。
显式 lock 锁

import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;/*** 测试Lock 锁*/
public class TestLock {public static void main(String[] args) {TestLock2 testLock2 = new TestLock2();new Thread(testLock2).start();new Thread(testLock2).start();new Thread(testLock2).start();}}class TestLock2 implements Runnable{private int ticketNum = 10;// 定义lock锁private final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();@Overridepublic void run() {while (true) {try {lock.lock(); // 加锁if (ticketNum > 0) {try {Thread.sleep(1000);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}System.out.println(ticketNum--);} else {break;}} finally {// 解锁lock.unlock();}}}
}

sychronize 和 lock区别

线程通信问题
生产者 消费者 模式


线程通信中需要的方法
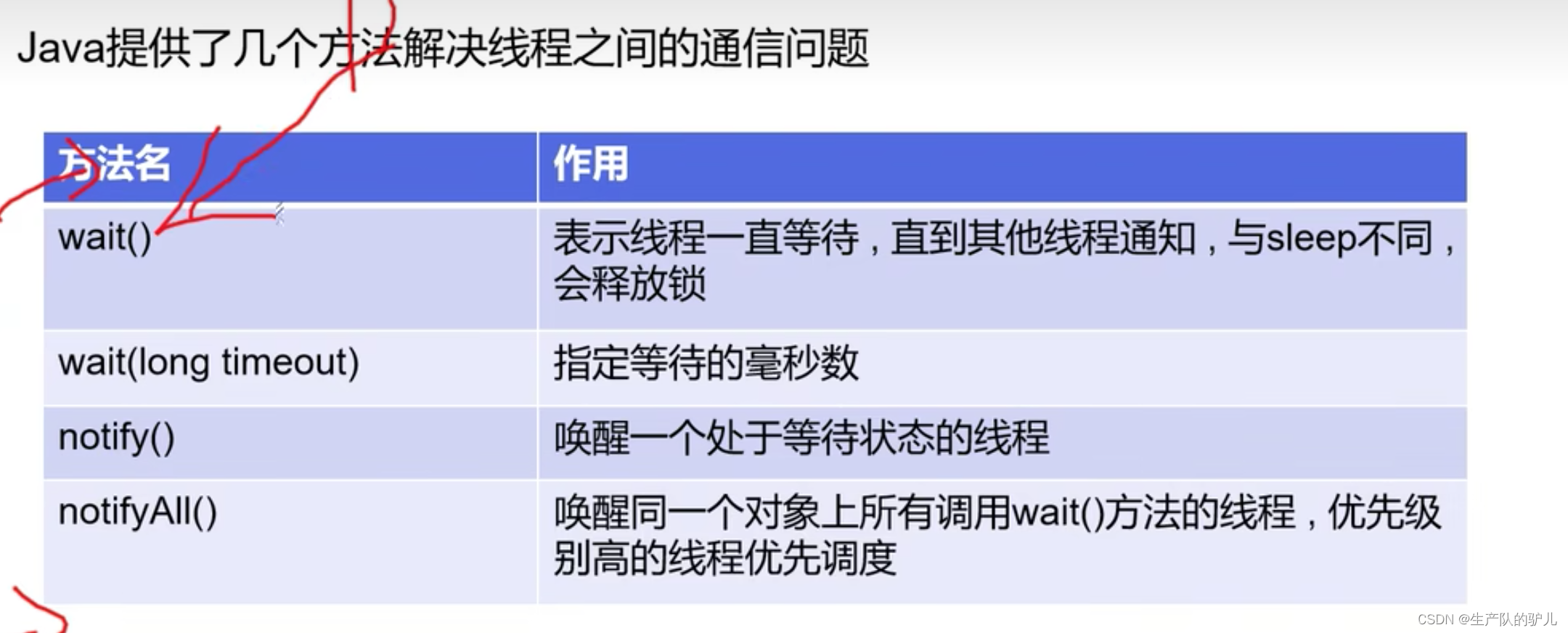
解决生产者消费者模式方法
方法1 管程法

先生产 100个,放到池子里,然后消费者消费。
这个池子 叫 缓冲区。
/*** 测试生产者消费者模型* 利用 缓冲区解决: 管程法** 生产者,消费者,产品,缓冲区** 生产者:* 消费者:* 产品:**/public class TestPC {public static void main(String[] args) {SynContainer container = new SynContainer();new Productor(container).start();new Cumsumer(container).start();}
}class Productor extends Thread{SynContainer synContainer;public Productor(SynContainer synContainer) {this.synContainer = synContainer;}@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {synContainer.push(new Chicken(i));System.out.println("生产了第" + i + "只鸡");}}
}
class Cumsumer extends Thread{SynContainer synContainer;public Cumsumer(SynContainer synContainer) {this.synContainer = synContainer;}@Overridepublic void run() {super.run();for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {long id = synContainer.pop().getId();System.out.println("消费了第" + id + "只鸡");}}
}
//产品
class Chicken extends Thread{int id;public Chicken(int id) {this.id = id;}public long getId() {return id;}
}
// 缓冲区
class SynContainer{// 需要一个容器大小Chicken[] chickens = new Chicken[10];// 容器已有产品计数int count = 0;// 生产者生产public synchronized void push(Chicken chicken){// 如果容器满了,等待消费者消费,没满,就加入if (count == chickens.length) {// 通知消费者消费try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {e.printStackTrace();}}chickens[count] = chicken;count++;this.notifyAll();}// 消费者消耗public synchronized Chicken pop(){// 为空,就通知生产者生产,等待,否则消费if (count == 0) {// 消费者等待生产者生产try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}count--;Chicken chicken1 = chickens[count];this.notifyAll();return chicken1;}
}
方法2 信号灯法
并发协作模型“生产者 / 消费者模式”–>信号灯法

/*** 测试生产者消费者问题2: 信号灯法, 标志位解决*/
public class TestPC2 {public static void main(String[] args) {TV tv = new TV();new Player(tv).start();new Watcher(tv).start();}}class Player extends Thread{TV tv;public Player(TV tv){this.tv = tv;}@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {if (i % 2 == 0) {this.tv.play("快乐大本营");} else {this.tv.play("抖音,记录美好生活");}}}
}class Watcher extends Thread{TV tv;public Watcher(TV tv) {this.tv = tv;}@Overridepublic void run() {for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++) {tv.watch();}}
}// 产品 --> 节目
class TV{// 演员表演。观众等待// 观众观看。演员观看String voice; // 表演的节目boolean flag = true;public synchronized void play(String voice) {if (!flag) {try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}System.out.println("演员表演了:" + voice);// 通知观众观看this.notifyAll(); // 通知唤醒this.voice = voice;this.flag = !this.flag;}// 观看public synchronized void watch(){if (flag) {try {this.wait();} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}System.out.println("观看了:" + voice);this.notifyAll();// 通知演员表演this.flag = !this.flag;}
}
线程池


import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;public class TestPool {public static void main(String[] args) {// 1. 创建服务,创建线程池// newFixedThreadPool 参数为 线程池大小ExecutorService service = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(10);// 执行service.execute(new MyThread());service.execute(new MyThread());service.execute(new MyThread());service.execute(new MyThread());// 2. 关闭链接service.shutdownNow();}
}class MyThread implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run() {System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());}
}
pool-1-thread-1
pool-1-thread-4
pool-1-thread-2
pool-1-thread-3
知识回顾
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;/*** 回归总结线程的创建*/
public class ThreadNew {public static void main(String[] args) {new MyThread1().start();new Thread(new MyThread2()).start();FutureTask futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new MyThread3());new Thread(futureTask).start();try {Integer integer = futureTask.get();System.out.println(integer);} catch (InterruptedException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);} catch (ExecutionException e) {throw new RuntimeException(e);}}}// 1. 继承Thread类
class MyThread1 extends Thread{@Overridepublic void run(){System.out.println("My Thread1");}
}//2. 实现Runnable接口
class MyThread2 implements Runnable{@Overridepublic void run(){System.out.println("My Thread2");}
}//3. 实现Callable接口
class MyThread3 implements Callable{@Overridepublic Integer call() throws Exception {return 100;}
}
上一篇:javaweb高校运动会管理系统