用javascript分类刷leetcode6.深度优先广度优先(图文视频讲解)
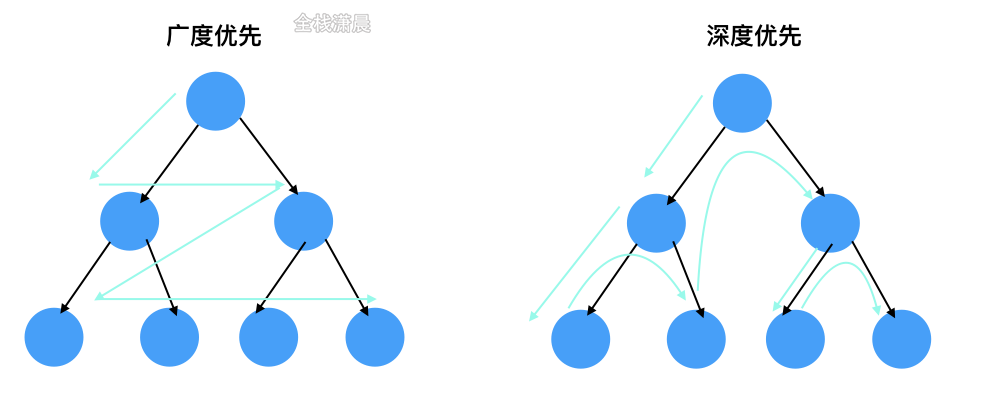
深度优先&广度优先
动画过大,点击查看
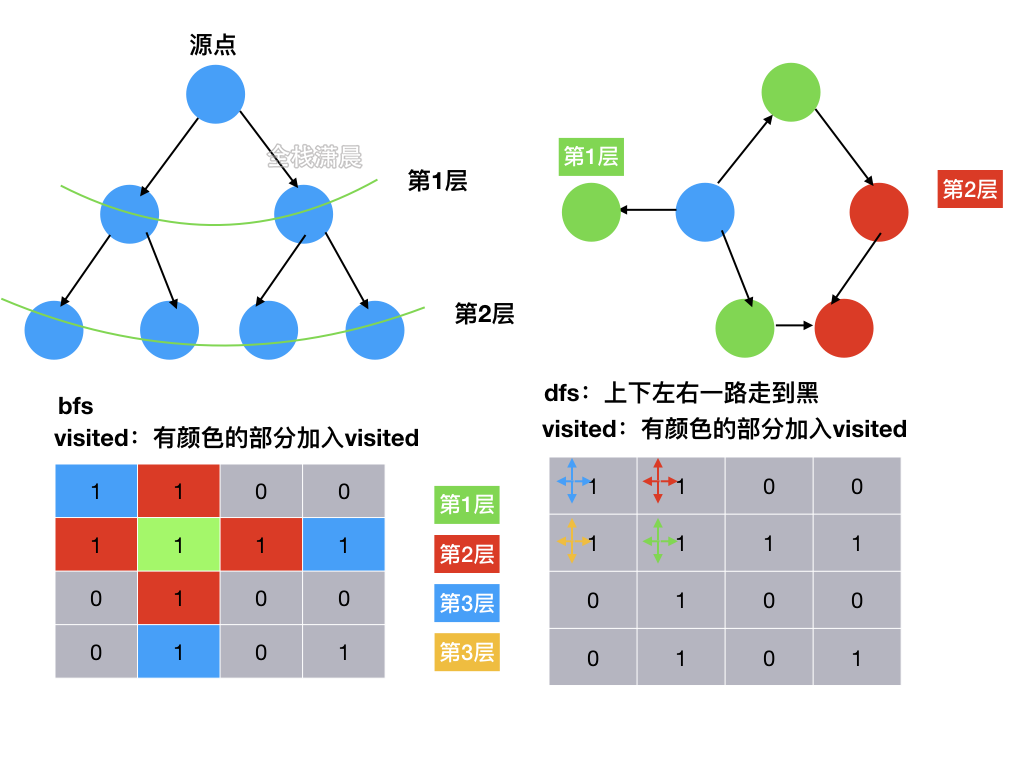
bfs:适用于层序遍历或者寻找最短路径的问。
//bfs伪代码模版
function bfs(graph, start, end) {queue = [];queue.append([start]);visited.add(start);while (queue) node = queue.pop();visited.add(node);process(node);nodes = generate_related_nodes(node);queue.add(nodes);
}
dfs:
//dfs伪代码模版
//递归
function dfs(node, visited) {visited.add(node);for (next_node in node.children()) {if (!next_node in visited) dfs(next_node, visited);}
}//非递归
function dfs(tree) {if (tree.root === null) {return [];}visited, (stack = []), [tree.node];while (stack) node = stack.pop();visited.add(node);process(node);nodes = generate_ralated_nodes(node);stack.push(nodes);
}
695. 岛屿的最大面积 (medium)
给你一个大小为 m x n 的二进制矩阵 grid 。
岛屿 是由一些相邻的 1 (代表土地) 构成的组合,这里的「相邻」要求两个 1 必须在 水平或者竖直的四个方向上 相邻。你可以假设 grid 的四个边缘都被 0(代表水)包围着。
岛屿的面积是岛上值为 1 的单元格的数目。
计算并返回 grid 中最大的岛屿面积。如果没有岛屿,则返回面积为 0 。
示例 1:
输入:grid = [[0,0,1,0,0,0,0,1,0,0,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,1,1,0,1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,0,1,0,0],[0,1,0,0,1,1,0,0,1,1,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,1,0,0,0],[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,1,1,0,0,0,0]]
输出:6
解释:答案不应该是 11 ,因为岛屿只能包含水平或垂直这四个方向上的 1 。
示例 2:输入:grid = [[0,0,0,0,0,0,0,0]]
输出:0提示:
m == grid.length
n == grid[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 50
grid[i][j] 为 0 或 1来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/max-area-of-island
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
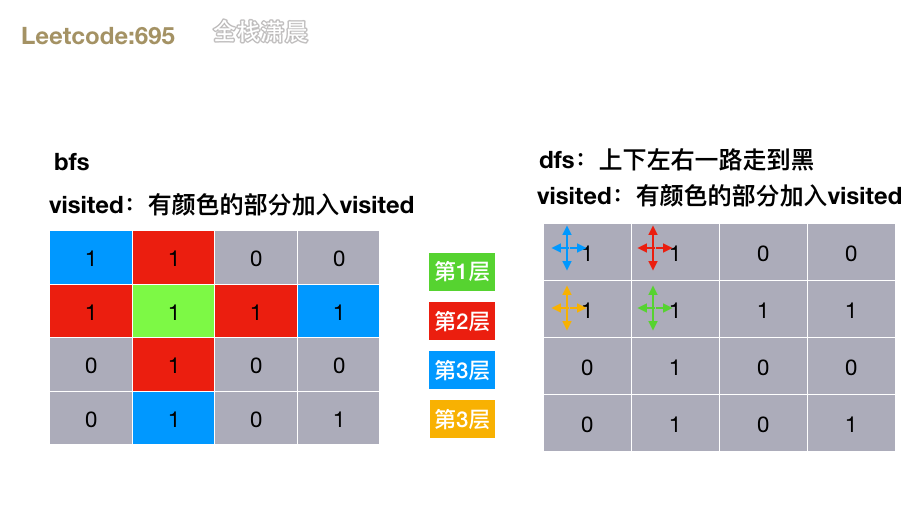
方法1.dfs
- 思路:深度优先,先循环网格, 当
grid[x][y] === 1时,将当前单元格置为0并上下左右不断递归,计算每个岛屿的大小,然后不断更新最大岛屿 - 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(mn),m、n分别是网格的长和宽。空间复杂度O(mn),递归最大深度
js:
var maxAreaOfIsland = function(grid) {let row = grid.length, col = grid[0].length;function dfs (x, y) {//越界判断 当grid[x][y] === 0时 直接返回if (x < 0 || x >= row || y < 0 || y >= col || grid[x][y] === 0) return 0;grid[x][y] = 0;//当grid[x][y] === 1时,将当前单元格置为0let ans = 1, dx = [-1, 1, 0, 0], dy = [0, 0, 1, -1];//方向数组for (let i = 0; i < dx.length; i++) {//上下左右不断递归,计算每个岛屿的大小ans += dfs(x + dx[i], y + dy[i]);}return ans;}let res = 0;for (let i = 0; i < row; i++) {for (let j = 0; j < col; j++) {res = Math.max(res, dfs(i, j));//循环网格 更新最大岛屿}}return res;
};
方法2.bfs
- 思路:广度优先,循环网格,不断将当前网格的坐标加入队列,如果当前网格对应的值是1,则置为0,然后向四周扩散,找到下一层的网格坐标,加入队列,直到队列为空
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(mn),m、n分别是网格的长和宽。空间复杂度O(mn),queue的大小
js:
var maxAreaOfIsland = function(grid) {let ans = 0, row = grid.length, col = grid[0].length;let dx = [1, -1, 0, 0], dy = [0, 0, 1, -1];//方向数组for (let i = 0; i < row; i++) {for (let j = 0; j < col; j++) {if (grid[i][j] === 0) continue;//循环网格,遇到0就跳过let queue = [[i, j]], curr = 0;//在队列中加入当前网格的值while (queue.length > 0) {let [x, y] = queue.shift();//不断出队//越界判断if (x < 0 || x >= row || y < 0 || y >= col || grid[x][y] === 0) continue;++curr;//更新岛屿的数量grid[x][y] = 0;//遍历过的网格置为0for (let k = 0; k < dx.length; k++) {//上下左右遍历,把下一层的节点加入队列queue.push([x + dx[k], y + dy[k]]);}}ans = Math.max(ans, curr);//更新最大岛屿面积}}return ans;
};
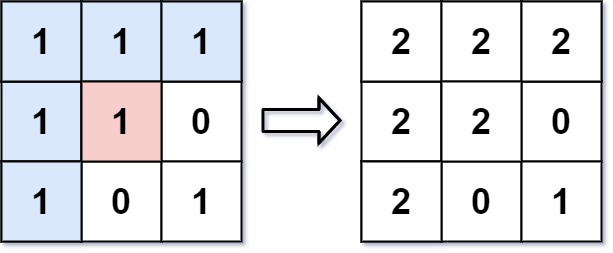
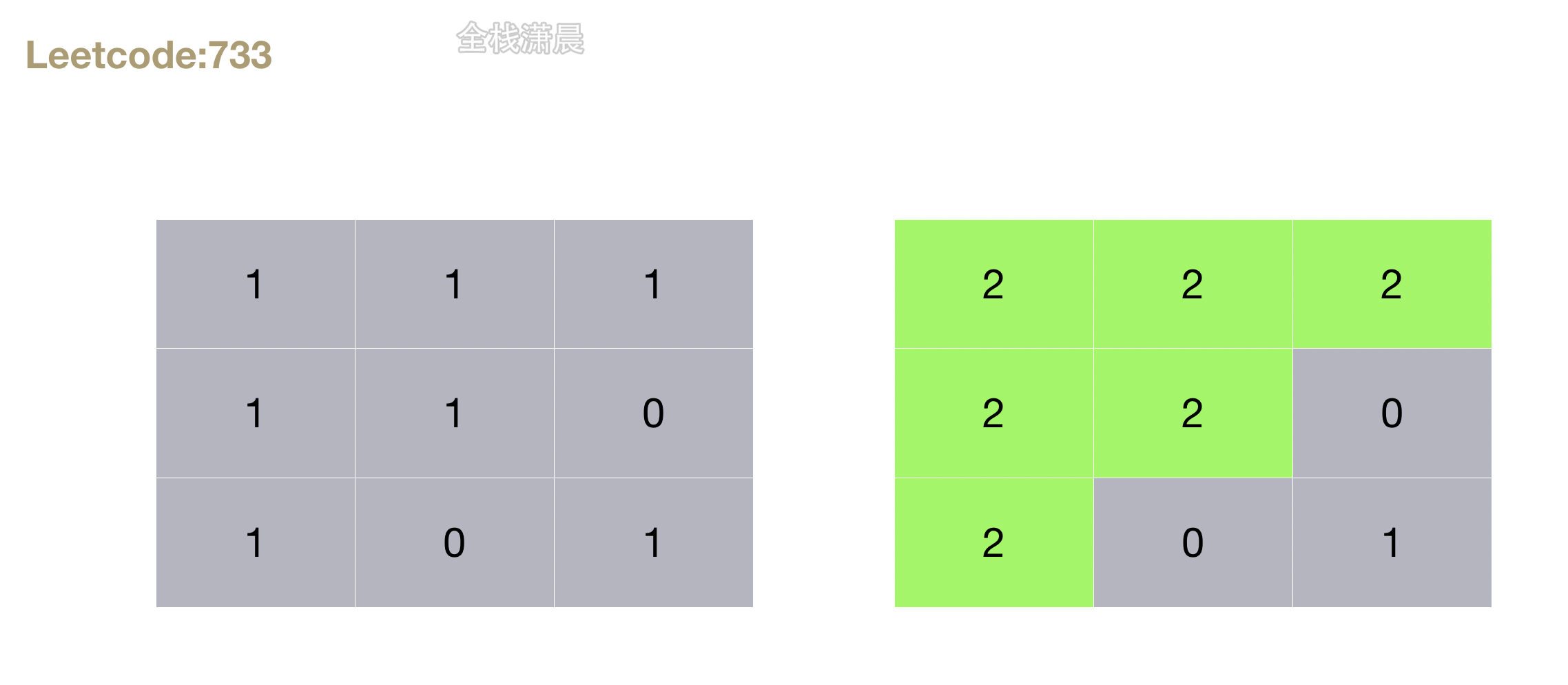
733. 图像渲染 (easy)
有一幅以 m x n 的二维整数数组表示的图画 image ,其中 image[i][j] 表示该图画的像素值大小。
你也被给予三个整数 sr , sc 和 newColor 。你应该从像素 image[sr][sc] 开始对图像进行 上色填充 。
为了完成 上色工作 ,从初始像素开始,记录初始坐标的 上下左右四个方向上 像素值与初始坐标相同的相连像素点,接着再记录这四个方向上符合条件的像素点与他们对应 四个方向上 像素值与初始坐标相同的相连像素点,……,重复该过程。将所有有记录的像素点的颜色值改为 newColor 。
最后返回 经过上色渲染后的图像 。
示例 1:
输入: image = [[1,1,1],[1,1,0],[1,0,1]],sr = 1, sc = 1, newColor = 2
输出: [[2,2,2],[2,2,0],[2,0,1]]
解析: 在图像的正中间,(坐标(sr,sc)=(1,1)),在路径上所有符合条件的像素点的颜色都被更改成2。
注意,右下角的像素没有更改为2,因为它不是在上下左右四个方向上与初始点相连的像素点。
示例 2:输入: image = [[0,0,0],[0,0,0]], sr = 0, sc = 0, newColor = 2
输出: [[2,2,2],[2,2,2]]提示:
m == image.length
n == image[i].length
1 <= m, n <= 50
0 <= image[i][j], newColor < 216
0 <= sr < m
0 <= sc < n
方法1.dfs
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(mn),m、n分别是网格的长和宽。空间复杂度O(mn),递归最大深度
js:
const floodFill = (image, sr, sc, newColor) => {const m = image.length;const n = image[0].length;const oldColor = image[sr][sc];if (oldColor == newColor) return image;const fill = (i, j) => {if (i < 0 || i >= m || j < 0 || j >= n || image[i][j] != oldColor) {return;}image[i][j] = newColor;fill(i - 1, j);fill(i + 1, j);fill(i, j - 1);fill(i, j + 1);};fill(sr, sc);return image;
};
方法2.bfs
- 复杂度:时间复杂度
O(mn),m、n分别是网格的长和宽。空间复杂度O(mn),递归最大深度
js:
const floodFill = (image, sr, sc, newColor) => {const m = image.length;const n = image[0].length;const oldColor = image[sr][sc];if (oldColor == newColor) return image;const queue = [[sr, sc]];while (queue.length) {const [i, j] = queue.shift();image[i][j] = newColor;if (i - 1 >= 0 && image[i - 1][j] == oldColor) queue.push([i - 1, j]);if (i + 1 < m && image[i + 1][j] == oldColor) queue.push([i + 1, j]);if (j - 1 >= 0 && image[i][j - 1] == oldColor) queue.push([i, j - 1]);if (j + 1 < n && image[i][j + 1] == oldColor) queue.push([i, j + 1]);}return image;
};
视频讲解:传送门
下一篇:Hadoop 组成